Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Calculate the change in angular momentum of the electron when it jumps from third orbit to first orbit in hydrogen atom.
(Take h = 6.33 × 10−34 Js)
उत्तर
According to Bohr's second postulate,
Angular momentum = `(nh)/(2 pi)`
For the first orbit, n1 = 1
∴ `L_1 = ((1)h)/(2 pi) = h/(2 pi)` ...(i)
For the third orbit, n3 = 3
∴ `L_3 = ((3)h)/(2 pi) = (3h)/(2 pi)` ...(ii)
When an electron jumps from 3rd orbit to 1st orbit, the change in angular momentum is
`L_3 - L_1 = (3 h)/(2 pi) - h/(2 pi)`
= `(2 h)/(2 pi)`
= `h / pi`
Putting h and π values, we get
Change in angular momentum = `(6.33 xx 10^-34)/3.142`
= 2.11 × 10−34 kg m2/s
The change in angular momentum of an electron when it jumps from the 3rd orbit to the 1st orbit in a hydrogen atom is 2.11 × 10−34 kg m2/s.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Obtain an expression for torque acting on a body rotating with uniform angular acceleration.
A 500 kg car takes a round turn of the radius of 50m with a velocity of 36 km/hr. The centripetal force is ______.
An electron(e) is revolving in a circular orbit of radius r in the hydrogen atom. The angular momentum of the electron is (M = magnetic dipole moment associated with it and m = mass of electron)
A stone of mass 1 kg is rotated in a horizontal circle of radius 0.5 m. If it makes `100/pi` rps, then its angular momentum is ______
A charged particle (charge = q: mass = m) is rotating in a circle of radius 'R' with uniform speed 'v'. The ratio of its magnetic moment (M) to the angular momentum (L) is ______
If the angular momentum of a body increases by 50%, then its kinetic energy of rotation increases by ______ (M.I. remains constant)
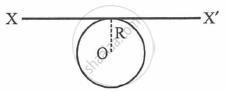
A thin metal wire of length 'L' and uniform linear mass density 'ρ' is bent into a circular coil with 'O' as centre. The moment of inertia of a coil about the axis XX' is ______.
The angular momentum of electron in hydrogen atom is proportional to ____________.
If the kinetic energy of rotation of a body is doubled, then its angular momentum ____________.
The ratio of the dimensions of Planck's constant to that of moment of inertia is the dimensions of ______.
A particle of mass m is rotating in a plane in a circular path of radius r. Its angular momentum is L. The centripetal force acting on the particle is ______.
If the angular momentum of an electron is `vec"J"` then the magnitude of the magnetic moment will be ____________.
A homogeneous disc of mass 2 kg and radius 15 cm is rotating about its axis (which is fixed) with an angular velocity of 4 radian/s. The linear momentum of the disc is ____________.
mass is whirled in a circular path with constant angular velocity and its linear velocity is v. If the string is now halved keeping the angular momentum same, the linear velocity is ______.
The direction of angular momentum of particle is ____________.
An electron of mass 'm' revolving around the nucleus in a circular orbit of radius 'r' has angular momentum 'L'. The magnetic field produced by the electron at the centre of the orbit is e = electric charge, µ0 = permeability of free space ____________.
A particle is revolving in anticlockwise sense along the circumference of a circle of radius 'r' with linear velocity 'v', then the angle between 'v' and angular velocity 'ω' will be ______.
If E, M and P are the kinetic energy, mass and linear momentum of a particle respectively, which of the following relations represents the angular momentum L of the particle when the particle rotates in a circle of radius R?
lf 'I' is the moment of inertia and 'L' is angular momentum of a rotating body, then `L^2/(2I)` is its ______.
Three-point masses each of mass 'M' are placed at the corners of an equilateral triangle of side 'a'. The moment of inertia of this system about an axis passing through one side of a triangle is ______.
An electron in an atom is revolving round the nucleus in a circular orbit of radius 5.3 × 10-11 m with a speed of 3 × 106 m/s. Find the angular momentum of electron.
A wheel of moment of inertia 2 kg m2 is rotating about an axis passing through centre and perpendicular to its plane at a speed 60 rad/s. Due to friction, it comes to rest in 5 minutes. The angular momentum of the wheel three minutes before it stops rotating is ______.
A disc of moment of inertia 'I1' is rotating in horizontal plane about an axis passing through a centre and perpendicular to its plane with constant angular speed 'ω1'. Another disc of moment of inertia 'I2' having zero angular speed is placed co-axially on a rotating disc. Now, both the discs are rotating with constant angular speed 'ω2'. The energy lost by the initial rotating disc is ______.
A particle of mass m = 5 unit is moving with a uniform speed v = 3`sqrt2` unit in the XY-plane along the line y = x + 4. The magnitude of the angular momentum about origin is ______.
Define moment of inertia.
