Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Consider the following cyclic process consist of isotherm, isochoric and isobar which is given in the figure.
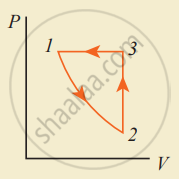
Draw the same cyclic process qualitatively in the V-T diagram where T is taken along the x-direction and V is taken along the y-direction. Analyze the nature of heat exchange in each process.
उत्तर
Process 1 to 2: increase in volume. So heat must be added.
Process 2 to 3: Volume remains constant. Increase in temperature. The given heat is used to increase the internal energy.
Process 3 to 1: Pressure remains constant. Volume and Temperature are reduced. Heat flows out of the system. It is an isobaric compression where the work is done on the system.

Explanation: In the graph, during the process (1 to 2), the gas undergoes isothermal expansion. It receives a certain amount of heat from its surroundings. It uses this heat in doing the work. Hence internal energy of the gas remains unchanged.
During the process represented by (2 to 3), the gas is heated at a constant volume. Since no work is done and volume does not change, the process is an isochoric process.
Since heat is transferred to the gas from the surroundings, the internal energy of the gas is increased. During the process represented by (3 to 1), the gas is compressed isobarically. Work is done on the gas. Since temperature drops internal energy is reached. Hence the gas gives up heat to the surroundings.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Answer in brief.
Why should a Carnot cycle have two isothermal two adiabatic processes?
For work done to be reversible, the process should be ______
Draw a p-V diagram showing positive work at constant pressure.
An ideal gas of volume 2 L is adiabatically compressed to (1/10)th of its initial volume. Its initial pressure is 1.01 x 105 Pa, calculate the final pressure. (Given 𝛾 = 1.4)
An ideal gas is expanded isothermally from volume V1 to volume V2 and then compressed adiabatically to original volume V1. If the initial pressure is P1, the final pressure is P3 and net work done is W, then ____________.
An ideal gas is made to go from a state A to stale B in the given two different ways (see figure) (i) an isobaric and then an isochoric process and (ii) an isochoric and then an isobaric process. The work done by gas in the two processes are W1 and W2 respectively. Then,

For an isothermal expansion of a perfect gas, the value of `(Delta "P")/"P"` is equal to ____________.
Which of the following processes is reversible?
Explain the thermodynamic process.
When an inflated ballon is suddenly burst, why is the emerging air slightly cooled?
