Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Define the functional group and complete the following table.
| S.I. No. | Functional Group | Compound | Formula |
| (1) | ______________ | _______________ |
C2H5OH |
| (2) | _______________ | _______________ | CH3CHO |
उत्तर
Functional group:
- The atom or group of atoms present in the molecule which determines the characteristic property of organic compounds is called the functional group.
- All organic compounds are considered as derivatives of hydrocarbons, it is formed by replacing one or more hydrogen atom in a molecule by some other atom.
- In methane CH4, if one hydrogen is replaced by an – OH group, then compound methyl alcohol. CH3.OH is formed. The – OH group is the alcoholic functional group
- After replacement, a new compound has functions i.e. properties different from the parent hydrocarbon.
| SR. No. | Functional Group | Compound | Formula |
| (1) | OH | Ethyl Alcohol | C2H5OH |
| (2) | CHO | Acetaldehyde |
CH3CHO |
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
What would be the electron dot structure of a molecule of sulphur which is made up of eight atoms of sulphur? (Hint – the eight atoms of sulphur are joined together in the form of a ring.)
An element L consists of molecules.
What type of bonding is present in the particles that make up L?
Write any three features and give two examples of covalent compounds
Name a carbon containing molecule which has two double bonds.
What would be the electron-dot structure of carbon dioxide which has the formula CO2?
Draw the electron-dot structure of HCl compound and state the type of bonding.
Draw the electron-dot structure of N2 and state the type of bonding.
Explain why, graphite can be used as a lubricant but diamond cannot.
Why are covalent compounds generally poor conductors of electricity?
Match the pairs.
| Group 'A' | Group 'B' |
| a. C2H6 | 1. Unsaturated hydrocarbon |
| b. C2H2 | 2. Molecular formula of an alcohol |
| c. CH4O | 3. Saturated hydrocarbon |
| d. C3H6 | 4. Triple bond |
Explain the following term with example.
Covalent bond
Explain the following:
Covalent compounds have low melting and boiling point.
Which of the following is a common characteristic of a covalent compound?
Complete the following activity.
Write the names of the hydrocarbons for the following structural formula.
(isobutylene, cyclohexane, propene, cyclohexene, cyclopentane, benzene, propyne, isobutane, propane)
| \[\begin{array}{cc}\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}\\ |\phantom{....}|\phantom{....}|\\\ce{H - C - C - C - H}\\ |\phantom{....}|\phantom{....}|\\\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H} \end{array}\] |
Complete the following activity.
Write the names of the hydrocarbons for the following structural formula.
(isobutylene, cyclohexane, propene, cyclohexene, cyclopentane, benzene, propyne, isobutane, propane)
| \[\begin{array}{cc} \phantom{..}\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}\\ \phantom{..}|\phantom{....}|\phantom{....}|\\ \ce{H - C - C- C- H}\\ \phantom{.}|\phantom{....}|\phantom{....}|\\ \ce{H - C - H}\\ |\\\ce{H}\end{array}\] |
Complete the following activity.
Write the names of the hydrocarbons for the following structural formula.
(isobutylene, cyclohexane, propene, cyclohexene, cyclopentane, benzene, propyne, isobutane, propane)
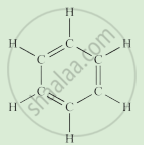 |
Carbon forms four covalent bonds by sharing its four valence electrons with four univalent atoms, e.g. hydrogen. After the formation of four bonds, carbon attains the electronic configuration of
In covalent bond formation, the sharing of ______ electrons takes place in their outermost shell.
What is a covalent bond?
Show the covalent bond formation in nitrogen molecule.
