Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Define the term wavefront. Using Huygen’s wave theory, verify the law of reflection.
उत्तर
In a region where the wave is propagating, the geometrical structure formed by joining all the points which are vibrating in same (absolute) phase are said to be wavefront Reflection of plane wave :
Consider a plane wave ABC incident at an angle ‘i’ on a reflecting surface ‘AD’. If v represents the speed of the wave in medium Δt is the time taken to move from ABC to B1C1 and also from B1C1 to point ‘D’. So, at the time when a disturbance of point ‘C’ reaches to point ‘D’ disturbance of point ‘A’ must have formed a hemispherical shape of radius 2vΔt and at point ‘B1’ it must have formed a hemispherical shape of radius vΔt. Drawing a common tangent from point ‘D’ to both of the above mentioned spherical envelopes we shall have DEF as reflected wavefront. Now, in ΔACD and ΔDFA
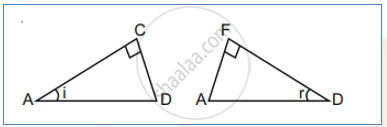
Side AD = AD and side CD = AF = 2vΔt
And ∠ACD = ∠DFA = 90°
so by RHS rule, both the triangles are congruent. Hence each corresponding parameter must be the same. Hence ∠CAD = i (angle of incidence) Must be the same as ∠FDA = r (angle of reflection) ∠i = ∠r
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
What is the shape of the wavefront in the following case?
Light diverging from a point source.
What is the shape of the wavefront in the following case?
The portion of the wavefront of light from a distant star was intercepted by the Earth.
Huygens' principle of secondary wavelets may be used to
(a) find the velocity of light in vacuum
(b) explain the particle behaviour of light
(c) find the new position of a wavefront
(d) explain Snell's Law
Derive the law of reflection using Huygen’s Wave Theory.
Define a wavefront. Using 'Huygens' principle, draw the shape of a refracted wavefront, when a plane wave is incident on a convex lens.
Huygen's conception of secondary waves ______.
Consider a point at the focal point of a convergent lens. Another convergent lens of short focal length is placed on the other side. What is the nature of the wavefronts emerging from the final image?
How is a wavefront different from a ray?
Using Huygen's wave theory of light, show that the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection. Draw a neat and labelled diagram.
What type of wavefronts are associated with a point source of light?
