Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Derive the law of reflection using Huygen’s Wave Theory.
उत्तर
Huygen’s wave theory :
Reflection at a plane surface : Consider a plane reflecting surface XY. Let AB be a plane wavefront of light incident obliquely on XY. When the incident wavefront touches XY at A, a secondary wavelet starts, spreading from A according to Huygens’ principle. Let the ray at B reach XY at D after a time t. If v is the speed of light in air then BD = vt. During this time t, the secondary wavelet from A spreads over a hemisphere of radius vt. with centre at A. Let CD be a tangent to this hemisphere. Then AC = BD. C and D are in the same phase. If we consider all the points between A and D, then CD will be tangential to all the secondary wavelets originating from these points at the end of t seconds. Hence CD is the reflected wavefront.
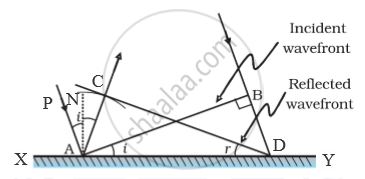
Draw AN normal to XY. Then
`anglePAN = i` , the angle of incidence , and `angleNAC = r` the angle of reflection
In triangles BAD and CDA
AC = BD = vt; AD is common, and `angleABD = angleACD = 90^circ` because the rays are normal to wavefronts.
`therefore` Triangles BAD and CDA are congruent
`therefore angleDAC = angleBDA , 90^circ - r = 90^circ - i`
OR `therefore i = r`
i.e , angle of incidence is equal to angle of reflection .
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
On the basis of Huygens' wave theory of light prove that velocity of light in a rarer medium is greater than velocity of light in a denser medium.
State Huygen's principle.
Define the term wavefront. Using Huygen’s wave theory, verify the law of reflection.
Define a wavefront. Using 'Huygens' principle, draw the shape of a refracted wavefront, when a plane wave is incident on a convex lens.
Relation between ray and wavefront is ______.
What is the geometrical shape of the wavefront for:
- Light diverging from a point source?
- The pattern of wavefront of the light from a distant star intercepted by earth?
For light diverging from a point source ______.
- the wavefront is spherical.
- the intensity decreases in proportion to the distance squared.
- the wavefront is parabolic.
- the intensity at the wavefront does not depend on the distance.
Is Huygen’s principle valid for longitudinal sound waves?
How is a wavefront different from a ray?
What type of wavefronts are associated with a source infinity?
