Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Derive the law of reflection using Huygen’s Wave Theory.
उत्तर
Huygen’s wave theory :
Reflection at a plane surface : Consider a plane reflecting surface XY. Let AB be a plane wavefront of light incident obliquely on XY. When the incident wavefront touches XY at A, a secondary wavelet starts, spreading from A according to Huygens’ principle. Let the ray at B reach XY at D after a time t. If v is the speed of light in air then BD = vt. During this time t, the secondary wavelet from A spreads over a hemisphere of radius vt. with centre at A. Let CD be a tangent to this hemisphere. Then AC = BD. C and D are in the same phase. If we consider all the points between A and D, then CD will be tangential to all the secondary wavelets originating from these points at the end of t seconds. Hence CD is the reflected wavefront.
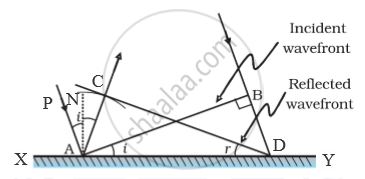
Draw AN normal to XY. Then
In triangles BAD and CDA
AC = BD = vt; AD is common, and
OR
i.e , angle of incidence is equal to angle of reflection .
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Explain the construction of plane wavefront using Huygens’ principle.
What is the shape of the wavefront in the following case?
Light diverging from a point source.
What is the shape of the wavefront in the following case?
The portion of the wavefront of light from a distant star was intercepted by the Earth.
Use Huygens' principle to verify the laws of refraction.
The refractive indices of water and diamond are
Using this principle draw a diagram to show how a plane wave front incident at the interface of the two media gets refracted when it propagates from a rarer to a denser medium. Hence verify Snell's law of refraction.
What is the phase difference between any two points lying on the same?
Is Huygen’s principle valid for longitudinal sound waves?
Consider a point at the focal point of a convergent lens. Another convergent lens of short focal length is placed on the other side. What is the nature of the wavefronts emerging from the final image?
Using Huygen's wave theory of light, show that the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection. Draw a neat and labelled diagram.
