Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Derive an expression for drift velocity of free electrons.
Derive an expression for drift velocity of electrons in a conductor. Hence deduce Ohm's law.
उत्तर
(i) Free electrons are in continuous random motion. They undergo change in direction at each collision and the thermal velocities are randomly distributed in all directions.
∴ Average thermal velocity,`u=(u_1+u_2+....+u_n)/n " is Zero".....(1)`
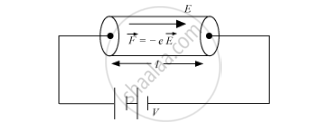
The electric field E exerts an electrostatic force ‘−Ee’.
Acceleration of each electron is,`veca=(-evecE)/m " ......(2)"`
Where,
m → Mass of an electron
e → Charge on an electron
Drift velocity,
`vec(v_d)=(vec(v_1)+vec(v_2)+....+vec(v_n))/n`
`vec(v_d)=((vec(u_1)+vecat_1)+(vec(u_2)+vecat_2)+....+(vec(u_n)+vecat_n))/n`
Where,
`vecu_1,vecu_2->` Thermal velocities of the electrons
`vecatau_1,vecatau_2->` Velocity acquired by electrons
τ1, τ2 → Time elapsed after the collision
`vec(v_d)=((vec(u_1)+vec(u_2)+...+vecu_n))/n+(veca(vec(t_1)+vec(t_2)+...vec(t_n)))/n`
Since `(vec(u_1)+vec(u_2)+....vec(u_n))/n=0`
∴ vd = a τ
Where,`t=(t_1+t_2+t_3....t_n)/n " is the average time elapsed"`
Substituting for a from equation (2),
`vec(v_d)=(-evecE)/mt " ...(4)"`
As, `E=V/l`
From (4) we can write
`v_d=(eV)/(ml)τ`
Also,
`I=An""ev_d`
Therefore,
`I=An""e((eV)/(ml)τ)=(An""e^2τ)/(ml) V`
`or V/I=(ml)/(An""e^2τ)=R` .... (5)
As we can see all the parameter on the R.H.S of the equation 5 are constant given temperature. And it is known as Resistance of the electric conductor.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Estimate the average drift speed of conduction electrons in a copper wire of cross-sectional area 1.0 × 10−7 m2 carrying a current of 1.5 A. Assume the density of conduction electrons to be 9 × 1028 m−3
(a) drift speed
(b) current density
(c) electric current
(d) electric field
When a current is established in a wire, the free electrons drift in the direction opposite to the current. Does the number of free electrons in the wire continuously decrease?
Electrons are emitted by a hot filament and are accelerated by an electric field, as shown in the figure. The two stops at the left ensure that the electron beam has a uniform cross-section.
The position-time relation of a particle moving along the x-axis is given by x = a - bt + ct2 where a, band c are positive numbers. The velocity-time graph of the particle is ______.
Amount of charge in coulomb required to deposit one gram equivalent of substance by electrolysis is:-
Is the momentum conserved when charge crosses a junction in an electric circuit? Why or why not?
The relaxation time τ is nearly independent of applied E field whereas it changes significantly with temperature T. First fact is (in part) responsible for Ohm’s law whereas the second fact leads to variation of ρ with temperature. Elaborate why?
Consider two conducting wires A and B of the same diameter but made of different materials joined in series across a battery. The number density of electrons in A is 1.5 times that in B. Find the ratio of the drift velocity of electrons in wire A to that in wire B.
