Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Derive th e equation of motion.
S = ut+ `1/2` at2,
Where the symbols have their usual meanings
उत्तर
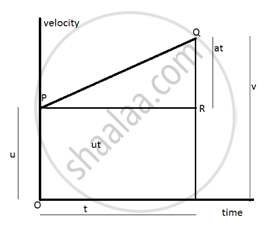
In figure we know
S = area of trapezium OSQP
Area of trapezium OSQP = 1/2 (sum of parallel sides) x perpendicular distance between them.
S = 1/2 (OP + SQ) x PR.
PR= QR/a= (QS-RS) / a
PR= (v - u)/a = t
So PR= t .
Substituting these values in expression of area of trapezium we get
S= 1/2 (u + v) xt
S = 1/2 (u +v) x (u - v)/a.
2aS = v2 - u2
v2 - u2 = 2 as.
This is known as third equation of motion.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Joseph jogs from one end A to the other end B of a straight 300 m road in 2 minutes 30 seconds and then turns around and jogs 100 m back to point C in another 1 minute. What are Joseph’s average speeds and velocities in jogging?
- from A to B and
- from A to C?
Abdul, while driving to school, computes the average speed for his trip to be 20 km h−1. On his return trip along the same route, there is less traffic and the average speed is 30 km h−1. What is the average speed for Abdul’s trip?
Name the physical quantity which gives us an idea of how slow or fast a body is moving.
A snail covers a distance of 100 metres in 50 hours. Calculate the average speed of snail in km/h.



A tortoise moves a distance of 100 metres in 15 minutes. What is the average speed of tortoise in km/h ?
A motorcyclist drives from place A to B with a uniform speed of 30 km h-1 and returns from place B to A with a uniform speed of 20 km h-1. Find his average speed.
Give an example of the motion of a body moving with a constant speed but with a variable velocity. Draw a diagram to represent such a motion.
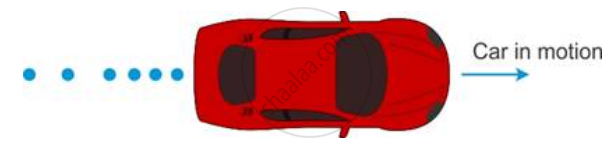
The diagram below shows the pattern of the oil on the road at a constant rate from a moving car. What information do you get from it about the motion of the car.
Express the following in m s-1.
1 km h-1
A car moving on a straight path covers a distance of 1 km due east in 100 s. What is the speed of the car?
