Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Derive the equation for effective focal length for lenses in contact.
उत्तर
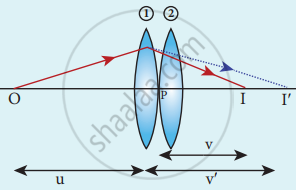
Lenses in contact
- Two lenses (1) and (2) having focal length are placed coaxially in contact.
- Lens equation for first equation be
`1/"v'" - 1/"u" = 1/"f"_1` - Lens equation for the second lens be
`1/"v" − 1/"v′" = 1/"f"_2` - Adding the above equation
`1/"v" - 1/"u" = 1/"f"_1 + 1/"f"_2` - If the combinations acts as single lens then,
`1/"v" - 1/"u" = 1/"f"` - On comparing,
`1/"F" = 1/"f"_1 + 1/"f"_2`
∴ For any number of lens in contact
`1/"f"_1 + 1/"f"_2 + 1/"f"_3 + ....`
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
An object is placed in front of a convex mirror of focal length of f and the maximum and minimum distance of an object from the mirror such that the image formed is real and magnified.
The radius of curvature of curved surface at a thin planoconvex lens is 10 cm and the refractive index is 1.5. If the plane surface is silvered, then the focal length will be.
What are primary focus and secondary focus of convex lens?
What are the sign conventions followed for lenses?
Obtain the equation for lateral magnification for thin lens.
What is power of a lens?
Derive the equation for thin lens and obtain its magnification.
Derive the equation for effective focal length for lenses in out of contact.
If the distance D between an object and screen is greater than 4 times the focal length of a convex lens, then there are two positions of the lens for which images are formed on the screen. This method is called conjugate foci method. If d is the distance between the two positions of the lens, obtain the equation for a focal length of the convex lens.
Find the ratio of the intensities of lights with wavelengths 500 nm and 300 nm which undergo Rayleigh scattering.
