Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Derive the relationship between Relative molecular mass and Vapour density.
उत्तर
(i) The Relative Molecular Mass of a gas or vapour is the ratio between the mass of one molecule of the gas or vapour to the mass of one atom of Hydrogen.
(ii) Vapour density is the ratio of the mass of a certain volume of a gas or vapour, to the mass of an equal volume of hydrogen, measured under the same conditions of temperature and pressure.
Vapour Density (V.D.) = `"Mass of a given volume of gas or vapour at S.T.P"/"Mass of the same volume of hydrogen"`.
(iii) According to Avogadro’s law, equal volumes of all gases contain an equal number of molecules. Thus, let the number of molecules in one volume = n, then
(iv) V.D at STP = `" Mass of molecules of a gas or vapour at S.T.P"/"Mass of 'n' ‘molecules of hydrogen"`
Cancelling ‘n’ which is common, you get
V.D = `"Mass of 1 molecule of a gas or vapour at S.T.P."/"Mass of 1 molecule of hydrogen"`.
(v) Since hydrogen is diatomic
V.D. = `"Mass of 1 molecule of a gas or vapour at S.T.P."/"Mass of 2 atoms of hydrogen"`
(vi) By comparing the definition of relative molecular mass and vapour density we can write as follows.
V.D. = `"Mass of 1 molecule of a gas or vapour at S.T.P."/(2 × "Mass of 1 atom of hydrogen")`
Relative molecular mass (hydrogen scale) = `"Mass of 1 molecule of a gas or vapour at STP."/"Mass of 1 atom of hydrogen"`
(vii) By substituting the relative molecular mass value in vapour density definition, we get
Vapour density (V.D.) = Relative molecular mass/2
⇒ 2 × vapour density = Relative molecular mass of a gas.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Write down the name of a compound represented by the following formula:
K2SO4
Write down the name of a compound represented by the following formula:
KNO3
Give the name of the element present in the following compound:
Hydrogen bromide
Give the name of the element present in the following compound:
Potassium sulphate
Calculate the number of molecules of sulphur (S8) present in 16 g of solid sulphur.
State the term.
The number of atoms present in a molecule of an element _________
Define: Atomic number
Define: Atomic number
What is meant by atomicity ? Explain with two examples.
What is the atomicity of the following ?
- Oxygen
- Ozone
- Neon
- Sulphur
- Phosphorus
- Sodium
Write the formulae of the following compounds. Also name the elements present in them.
- Water
- Ammonia
- Methane
- Sulphur dioxide
- Ethanol
What is the difference between the molecule of an element and the molecule of a compound ? Give one
example of each.
What are (i) ionic compounds, and (ii) molecular compounds ? Give two examples of each type of compounds.
An element X forms the following compounds with hydrogen, carbon and oxygen :
H2X, CX2, XO2, XO3
State the three valencies of element X which are illustrated by these compounds.
Calculate the mass of 3.011 × 1024 atoms of carbon.
Correct the following statement:
A molecule of sulphur is monoatomic.
Why are the symbols and formulae of substances important?
Give one example of a polyatomic molecule.
State the atomicity of the following:
Neon
State the atomicity of the following:
Oxygen
State the atomicity of the following:
Sulphur
State true of false. If false, give the correct statement.
NaCl represents one molecule of sodium chloride.
Classify the following molecules as the molecules of element or compound
| 1. |  |
|
| 2. |  |
|
| 3. | 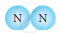 |
|
| 4. | 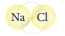 |
Two elements sometimes can form more than one compound.
Give any two examples for heterodiatomic molecules.
Write any two classifications of a molecule.
