Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Discuss the following case:
Source in motion and Observer at rest
- Source moves towards observer
- Source moves away from the observer
उत्तर
(a) Source moves towards die observer-
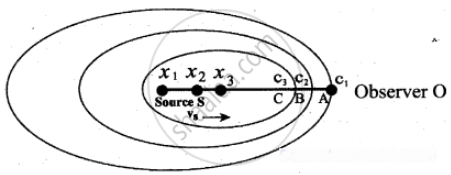
Source S moves towards an observer O (right) with velocity
Suppose a source S moves to the right (as shown in Figure) with a velocity vs and let the frequency of the sound waves produced by the source be fs. It is assumed that the velocity of sound in a medium is v.
Suppose a source S moves to the right (as shown in Figure) with a velocity vs and let the frequency of the sound waves produced by the source be fs. It is assumed that the velocity of sound in a medium is v.
The compression (sound wavefront) produced by the source S at three successive instants of time are shown in the Figure. When S is at position x1 the compression is at C1. When S is at position x2, the compression is at C2 and similarly for x3 and C3.
It is meant that the wavelength decreases when the source S moves towards the observer O. But frequency is inversely related to wavelength and therefore, frequency increases.
Calculation:
Let λ be the wavelength of the source S as measured by the observer when S is at position x1 and λ’ be the wavelength of the source observed by the observer when S moves to position x2.
Then the change in wavelength is ∆λ = λ – λ’ = vst, where t is the time taken by the source to travel between x1 and x2 Therefore,
λ’ = λ – vst … (1)
But t = \[\frac{λ}{v}\] … (2)
On substituting equations (2) in equation (1), we get.
`lambda' = lambda(1 - "v"_"s"/"v")`
Since frequency is inversely proportional to wavelength, we have
`"f"' = "v"_"s"/(lambda')` and f = `"v"_"s"/lambda`
Hence `"f"' = "f"/((1 - "v"_"s"/"v"))` ...(3)
Since, `"v"_"s"/"v"` << 1, by using the binomial expansion and retaining only first order in `"v"_"s"/"v"`, we get
`"f"' = "f"(1 + "v"_"s"/"v")` ...(4)
(b) Source moves away from the observer-
Since the velocity of the source is opposite in direction when compared to case (a), hence by changing the sign of the velocity of the source in the above case i.e., by substituting (vs → – v ) in equation (1), we get
`"f"' = "f"/((1 + "v"_"s"/"v"))` ....(5)
Using binomial expansion again, we get
`"f"' = "f"(1 - "v"_"s"/"v")` .....(6)
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A narrow sound pulse (for example, a short pip by a whistle) is sent across a medium. (a) Does the pulse have a definite (i) frequency, (ii) wavelength, (iii) speed of propagation? (b) If the pulse rate is 1 after every 20 s, (that is the whistle is blown for a split of second after every 20 s), is the frequency of the note produced by the whistle equal to 1/20 or 0.05 Hz
The engine of a train sounds a whistle at frequency v. The frequency heard by a passenger is
The sound emitted from the siren of an ambulance has a frequency of 1500 Hz. The speed of sound is 340 m/s. Calculate the difference in frequencies heard by a stationary observer if the ambulance initially travels towards and then away from the observer at a speed of 30 m/s.
N tuning forks are arranged in order of increasing frequency and any two successive tuning forks give n beats per second when sounded together. If the last fork gives double the frequency of the first (called as octave), Show that the frequency of the first tuning fork is f = (N – 1)n.
A bus is moving with a velocity of 5 m is towards a wall. The driver blows the horn of frequency 165 Hz. If the speed of sound in air is 335 m is, then after reflection of sound wave, the number of beats per second heard by the passengers in the bus will be ______.
An observer moves towards a stationary source of sound with a velocity one-fifth of the velocity of sound. The percentage increase in the apparent frequency heard by the observer will be ______.
If a star appearing yellow starts accelerating towards the earth, its colour appears to be turned ______.
A source of sound is moving towards a stationary observer with velocity 'Vs' and then moves away with velocity 'Vs'. Assume that the medium through which the sound waves travel is at rest, if 'V' is the velocity of sound and 'n' is the frequency emitted by the source, then the difference between the apparent frequencies heard by the observer is ______.
When a sound source of frequency n is approaching a stationary observer with velocity u than the apparent change in frequency is Δn1 and when the same source is receding with velocity u from the stationary observer than the apparent change in frequency is Δn2. Then ______.
A whistle producing sound waves of frequencies 9500 Hz and above is approaching a stationary person with speed v ms-1. The velocity of sound in air is 300 ms-1. If the person can hear frequencies up to a maximum of 10,000 HZ, the maximum value of v up to which he can hear the whistle is ______.
