Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Discuss the ideal gas laws.
उत्तर
Boyle’s law: For a given gas at low pressure (density) kept in a container of volume V, experiments revealed the following information.
When the gas is kept at a constant temperature, the pressure of the gas is inversely proportional to the volume `"P" ∝ 1/"V"`
Charles’ law: When the gas is kept at constant pressure, the volume of the gas is directly proportional to absolute temperature V ∝ T.
By combining these two equations we have PV = CT.
Here C is a positive constant.
We can infer that C is proportional to the number of particles in the gas container by considering the following argument. If we take two containers of the same type of gas with the same volume V, same pressure P and same temperature T, then the gas in each container obeys the above equation. PV = CT. If the two containers of gas are considered as a single system, then the pressure and temperature of this combined system will be the same but the volume will be twice and the number of particles will also be double.
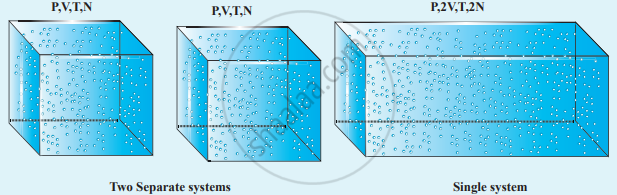
For this combined system, V becomes 2V, so C should also double to match with the ideal gas equation `("P"(2"V"))/"T"` = 2C. It implies that C must depend on the number of particles in the gas and also should have the dimension of `["PV"/"T"]` = JK−1. So we can write the constant C as k times the number of particles N.
Here k is the Boltzmann constant (1.381 × 10-23 JK-1) and it is found to be a universal constant. So the ideal gas law can be stated as follows
PV = NkT …..............(1)
The equation (1) can also be expressed in terms of mole.
Suppose if the gas contains p mole of particles then the total number of particles can be written as
N = µNA …….........(2)
where NA is Avogadro number (6.023 × 1023 mol-1)
Substituting for N from equation (2), the equation (1) becomes PV = µNAkT.
Here NAk = R called the universal gas constant and its value is 8.314 J/mol. K
So the ideal gas law can be written for µ mole of gas as
PV = μRT ...........…(3)
This is called the equation of state for an ideal gas. It relates the pressure, volume and temperature of the thermodynamic system at equilibrium.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Choose the correct option.
If two temperatures differ by 25° C on Celsius scale, the difference in temperature on Fahrenheit scale is
Write the unit of specific heat capacity.
Define molar specific heat capacity.
What is a thermal expansion?
Give the expression for volume thermal expansion.
Define latent heat capacity.
Write the unit of latent heat capacity.
Explain Calorimetry and derive an expression for final temperature when two thermodynamic systems are mixed.
The temperature of a uniform rod of length L having a coefficient of linear expansion αL is changed by ∆T. Calculate the new moment of inertia of the uniform rod about the axis passing through its center and perpendicular to an axis of the rod.
Another name for thermal energy is ______
