Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Explain the meaning of heat and work with suitable examples.
उत्तर
Meaning of heat: When an object at a higher temperature is placed in contact with another object at a lower temperature, there will be a spontaneous flow of energy from the object at a higher temperature to the one at a lower temperature. This energy is called heat. This process of energy transfer from higher temperature objects to lower temperature objects is called heating. Due to the flow of heat sometimes the temperature of the body will increase or sometimes it may not increase.
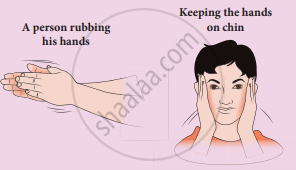
Meaning of work: When you rub your hands against each other the temperature of the hand's increases. You have done some work on your hands by rubbing. The temperature of the hands increases due to this work. Now if you place your hands on the cheek, the temperature of the cheek increases. This is because the hands are at a higher temperature than the cheek. In the above example, the temperature of the hands is increased due to work, and the temperature of the cheek is increased due to heat transfer from the hands to the chin. It is shown in the Figure. By doing work on the system, the temperature in the system will increase and sometimes may not. Like heat, work is also not a quantity and through the work-energy is transferred to the system. So we cannot use the word ‘the object contains more work’ or ‘less work’.
Either the system can transfer energy to the surrounding by doing work on surrounding or the surrounding may transfer energy to the system by doing work on the system. For the transfer of energy from one body to another body through the process of work, they need not be at different temperatures.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Define emissive power and coefficient of emmision of a body.
Compute the temperature at which the r.m.s. speed of nitrogen molecules is 832 m/s. [Universal gas constant, R = 8320 J/k mole K, molecular weight of nitrogen = 28.]
The substance which allows heat radiations to pass through is _______.
(A) iron
(B) water vapour
(C) wood
(D) dry air
The kinetic energy per molecule of a gs at temperature T is ________.
(a) `(3/2)RT`
(b) `(3/2)K_BT`
(c) `(2/3) RT`
(d) `(3/2)("RT"/M)`
It is said that mercury is used in defining the temperature scale because it expands uniformly with temperature. If the temperature scale is not yet defined, is it logical to say that a substance expands uniformly with temperature?
If the temperature of a uniform rod is slightly increased by ∆t, its moment of inertia I about a line parallel to itself will increase by
Is heat a conserved quantity?
Two bodies at different temperatures are mixed in a calorimeter. Which of the following quantities remains conserved?
Temperature in the form of energy.
The normal temperature of our body is 37°C.
