Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Find the number of molecules of an ideal gas in a volume of 1.000 cm3 at STP.
उत्तर
Here,
Volume of ideal gas at STP = 22.4 L
Number of molecules in 22.4 L of ideal gas at STP = 6.022\[\times\]1023
Number of molecules in 22.4\[\times\]103 cm3 of ideal gas at STP = 6.022\[\times\]1023
Now,
Number of molecules in 1 cm3 of ideal gas at STP =\[\frac{6 . 022 \times {10}^{23}}{22 . 4 \times {10}^3} = 2 . 688 \times {10}^{19}\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
When we place a gas cylinder on a van and the van moves, does the kinetic energy of the molecules increase? Does the temperature increase?
If the molecules were not allowed to collide among themselves, would you expect more evaporation or less evaporation?
The temperature and pressure at Simla are 15.0°C and 72.0 cm of mercury and at Kalka these are 35.0°C and 76.0 cm of mercury. Find the ratio of air density at Kalka to the air density at Simla.
Use R=8.314J K-1 mol-1
The mean speed of the molecules of a hydrogen sample equals the mean speed of the molecules of a helium sample. Calculate the ratio of the temperature of the hydrogen sample to the temperature of the helium sample.
Use R = 8.314 JK-1 mol-1
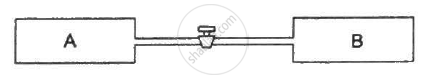
Figure shows two vessels A and B with rigid walls containing ideal gases. The pressure, temperature and the volume are pA, TA, V in the vessel A and pB, TB, V in the vessel B. The vessels are now connected through a small tube. Show that the pressure p and the temperature T satisfy `Ρ/T = 1/2 ({P_A}/{T_A}+{P_B}/{T_B))` when equilibrium is achieved.
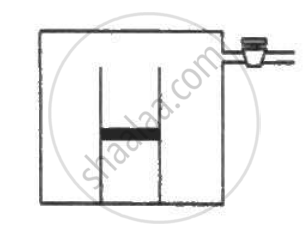
An ideal gas is kept in a long cylindrical vessel fitted with a frictionless piston of cross-sectional area 10 cm2 and weight 1 kg in figure. The vessel itself is kept in a big chamber containing air at atmospheric pressure 100 kPa. The length of the gas column is 20 cm. If the chamber is now completely evacuated by an exhaust pump, what will be the length of the gas column? Assume the temperature to remain constant throughout the process.
An adiabatic cylindrical tube of cross-sectional area 1 cm2 is closed at one end and fitted with a piston at the other end. The tube contains 0.03 g of an ideal gas. At 1 atm pressure and at the temperature of the surrounding, the length of the gas column is 40 cm. The piston is suddenly pulled out to double the length of the column. The pressure of the gas falls to 0.355 atm. Find the speed of sound in the gas at atmospheric temperature.
Calculate the average molecular kinetic energy
- per kmol
- per kg
- per molecule
of oxygen at 127°C, given that the molecular weight of oxygen is 32, R is 8.31 J mol−1K−1 and Avogadro’s number NA is 6.02 × 1023 molecules mol−1.
The emissive power of a sphere of area 0.02 m2 is 0.5 kcal s-1m-2. What is the amount of heat radiated by the spherical surface in 20 seconds?
If the density of nitrogen is 1.25 kg/m3 at a pressure of 105 Pa, find the root mean square velocity of nitrogen molecules.
Compare the rate of radiation of metal bodies at 727 °C and 227 °C.
A metal cube of length 4 cm radiates heat at the rate of 10 J/s. Find its emissive power at a given temperature.
The graph of kinetic energy against the frequency v of incident light is as shown in the figure. The slope of the graph and intercept on X-axis respectively are ______.
Average kinetic energy of H2 molecule at 300K is 'E'. At the same temperature, average kinetic energy of O2 molecule will be ______.
The average translational kinetic energy of a molecule in a gas is 'E1'. The kinetic energy of the electron (e) accelerated from rest through p.d. 'V' volt is 'E2'. The temperature at which E1 = E2 is possible, is ______.
An ideal gas in a container of volume 500 cc is at a pressure of 2 × 105 N/m2. The average kinetic energy of each molecule is 6 × 10−21 J. The number of gas molecules in the container is ______.
A gas mixture consists of molecules of types A, B and C with masses mA > mB > mC. Rank the three types of molecules in decreasing order of average K.E.
According to the kinetic theory of gases, at a given temperature, molecules of all gases have the same ______.
