Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Draw all the isomers (geometrical and optical) of [Co(NH3)2Cl2(en)]+.
उत्तर
(i)
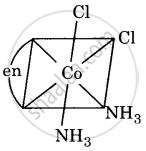
(ii)
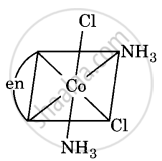
(iii)
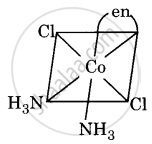
(iv)
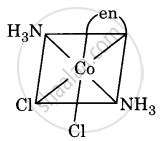
All are asymmetric. Hence, all will show optical isomerism, i.e. d(+) and l(-) forms, which are non-superimposable mirror images.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Define the following term:
Anomers
Indicate the types of isomerism exhibited by the following complex and draw the structures for these isomers:
[Co(en)3]Cl3
Draw all the isomers (geometrical and optical) of [Co(NH3)Cl(en)2]2+.
Write the structures of optical isomers of the complex ion `[Co(en)_2Cl_2]^+`
Draw the geometrical isomers of complex \[\ce{[Pt(en)2Cl2]^2+}\].
What type of structural isomers are [Co(NH3)5 Br] SO4 and [Co(NH3)5 SO4]Br? Give a chemical test to distinguish the isomers.
Name the type of isomerism exhibited by the following pairs of compound:
(1) (C2H5)2NH and CH3-NH-C3H7
(2) 1 – butanol and 2 methyl-1 -propanol.
Name the type of isomerism shown by the following pair of compounds:
[CoCl(H2O)(NH3)4]Cl2 and [CoCl2(NH3)4]Cl.H2O
Identify the optically active compounds from the following:
(i) \[\ce{[Co(en)3]^{3+}}\]
(ii) \[\ce{[trans - [Co(en)2Cl2]^+}\]
(iii) \[\ce{cis - [Co(en)2Cl2]^+}\]
(iv) \[\ce{[Cr(NH3)5Cl]}\]
The complex [(Pt(Py)(NH3)BrCl] will have how many geometrical isomers?
Draw the geometrical isomers of [Co(en)2Cl2]2+. Which geometrical isomer of [Co(en)2Cl2]2+ is not optically active and why?
Which of the following molecules has a chiral centre correctly labelled with an asterisk (*)?
Assertion (A): Trans [CrCl2(ox)2]3− shows optical isomerism.
Reason (R): Optical isomerism is common in octahedral complexes involving didentate ligands.
Indicate the types of isomerism exhibited by the following complexes and draw the structures for these isomers:
[Pt(NH3)(H2O)Cl2 ]
Indicate the type of isomerism exhibited by the following complex and draw the structure for this isomer:
[Pt(NH3)(H2O)Cl2]
Indicate the type of isomerism exhibited by the following complex and draw the structure for this isomer: \[\ce{[Pt(NH3)(H2O)Cl2]}\]
Indicate the types of isomerism exhibited by the following complexes and draw the structure for these isomer:
\[\ce{[Pt(NH3)(H2O)Cl2]}\]
Indicate the type of isomerism exhibited by the following complex and draw the structure for the isomer:
\[\ce{[Pt(NH3 )(H2O)Cl2]}\]
