Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Enumerate three most characteristic criteria for designating a Mendelian population.
उत्तर
Population must be sufficiently large with potentialities for free flow of genetic material among individuals (through sexual reproduction). Migration should either be nil or negligible.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
What does the following equation represent? Explain.
p2 + 2pq + q2 = 1
Very short answer question.
State the Hardy – Weinberg equilibrium.
In a population, Hardy Weinberg equilibrium is disturbed by following factors EXCEPT ______.
For the MN-blood group system, the frequencies of M and N alleles are 0.7 and 0.3, respectively. The expected frequency of MN-blood group bearing organisms is likely to be ______.
Among the five factors that are known to affect Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium, three factors are gene flow, genetic drift and genetic recombination. What are the other two factors?
At a particular locus, the frequency of allele A is 0.8, and that of allele a is 0.2. What would be the frequency of heterozygotes in a random mating population at equilibrium?
The graphs below show three types of natural selection. The shaded areas marked with arrows show the individuals in the population who are not selected. The dotted vertical lines show the statistical means.
 |
 |
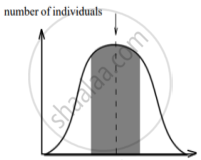 |
| character Graph A |
character Graph B |
character Graph C |
- What names are given to the types of selection shown in graphs A, B and C?
- After the selection has operated for several generations in the above populations indicated as, Graph A, B and C, graphically illustrate the probable results.
Explain Hardy-Weinberg's principle
A population of 200 fruit flies is in Hardy Weinberg equilibrium. The frequency of the allele (a) 0.4. Calculate the following:
The number of carrier fruit flies.
The black colour on the beak of finches dominates over the yellow colour. There are 210 individuals with the genotype DD, 245 individuals with the genotype Dd and 45 individuals with the genotype dd. Deduce the frequency of individuals with dominant, heterozygous, and recessive traits.
