Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Estimate the average thermal energy of a helium atom at room temperature (27 °C).
उत्तर
At room temperature, T = 27°C = 300 K
Average thermal energy = `3/2` kT
Where k is Boltzmann constant = 1.38 × 10–23 m2 kg s–2 K–1
`therefore 3/2kT = 3/2 xx 1.38 xx 10^(-38) xx 300`
= 6.21 × 10–21J
Hence, the average thermal energy of a helium atom at room temperature (27°C) is 6.21 × 10–21 J.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The figure shows the plot of PV/T versus Pfor 1.00×10–3 kg of oxygen gas at two different temperatures.
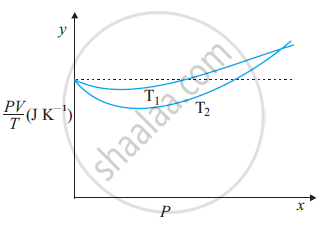
(a) What does the dotted plot signify?
(b) Which is true: T1 > T2 or T1 < T2?
(c) What is the value of PV/T where the curves meet on the y-axis?
(d) If we obtained similar plots for 1.00 ×10–3 kg of hydrogen, would we get the same value of PV/T at the point where the curves meet on the y-axis? If not, what mass of hydrogen yields the same value of PV/T (for low pressure high temperature region of the plot)? (Molecular mass of H2 = 2.02 u, of O2 = 32.0 u, R = 8.31 J mo1–1 K–1.)
Estimate the average thermal energy of a helium atom at the temperature of 10 million Kelvin (the typical core temperature in the case of a star).
At what temperature is the root mean square speed of an atom in an argon gas cylinder equal to the rms speed of a helium gas atom at – 20 °C? (atomic mass of Ar = 39.9 u, of He = 4.0 u).
During the practical session in the lab when hydrogen sulphide gas having offensive odour is prepared for some test, we can smell the gas even 50 metres away. Explain the phenomenon.
Name or state the following:
An equation used in chemical calculations which gives a simultaneous effect of changes of temperature and pressure on the volume of a given mass of dry gas
Give reason for the following:
Temperature remaining constant the product of the vol. & the press, of a given mass of dry gas is a constant.
Show that for diatomic gas the ratio of the two specific heats is 7:5.
The equation of state for 2g of oxygen at a pressure 'P' and temperature 'T', when occupying a volume 'V' will be ______.
Three vessels of equal capacity have gases at the same temperature and pressure. The first vessel contains neon (monatomic), the second contains chlorine (diatomic), and the third contains uranium hexafluoride (polyatomic).
Do the vessels contain an equal number of respective molecules?
The volume V of an enclosure contains a mixture of three gases, 16 g of oxygen, 28 g of nitrogen and 44 g of carbon dioxide at absolute temperature T. Consider R as universal gas constant. The pressure of the mixture of gases is ______.
