Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Estimate the total number of air molecules (inclusive of oxygen, nitrogen, water vapour and other constituents) in a room of capacity 25.0 m3 at a temperature of 27 °C and 1 atm pressure
उत्तर १
Volume of the room, V = 25.0 m3
Temperature of the room, T = 27°C = 300 K
Pressure in the room, P = 1 atm = 1 × 1.013 × 105 Pa
The ideal gas equation relating pressure (P), Volume (V), and absolute temperature (T) can be written as:
PV = kBNT
Where,
KB is Boltzmann constant = 1.38 × 10–23 m2 kg s–2 K–1
N is the number of air molecules in the room
`:. N = (PV)/(k_BT)`
`= (1.013xx10^5xx25)/(1.38xx10^(-23)xx300) = 6.11 xx 10^(26)` molecules
Therefore, the total number of air molecules in the given room is 6.11 × 1026.
उत्तर २
Here, Volume of room, `V= 25.0 m^3`, temperature, `T = 27 ^@C = 300 K` and
Pressure, `P = 1 "atm" = 1.01 xx 10^5 Pa`
According to gas equation, `PV = muRT = muN_A.k_BT`
Hence, total number of air molecules in the volume of given gas
`N = mu.N_A = PV/K_BT`
`:. N = (1.01 xx 10^5 xx25.0)/((1.38 xx 10^(-23))xx300) = 6.1 xx 10^(26)`
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The figure shows the plot of PV/T versus Pfor 1.00×10–3 kg of oxygen gas at two different temperatures.
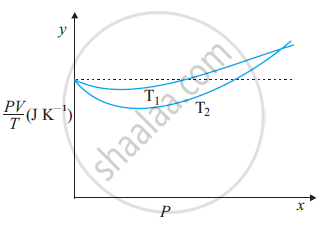
(a) What does the dotted plot signify?
(b) Which is true: T1 > T2 or T1 < T2?
(c) What is the value of PV/T where the curves meet on the y-axis?
(d) If we obtained similar plots for 1.00 ×10–3 kg of hydrogen, would we get the same value of PV/T at the point where the curves meet on the y-axis? If not, what mass of hydrogen yields the same value of PV/T (for low pressure high temperature region of the plot)? (Molecular mass of H2 = 2.02 u, of O2 = 32.0 u, R = 8.31 J mo1–1 K–1.)
What do you understand by gas?
Give reasons for the following:
Gas fills the vessel completely in which it is kept.
Correct the following statement:
0°C is equal to zero Kelvin.
Give reason for the following:
Temperature remaining constant the product of the vol. & the press, of a given mass of dry gas is a constant.
The average energy per molecule is proportional to ______
Show that for diatomic gas the ratio of the two specific heats is 7:5.
Estimate the average thermal energy of a helium atom at room temperature (27 °C).
The volume V of an enclosure contains a mixture of three gases, 16 g of oxygen, 28 g of nitrogen and 44 g of carbon dioxide at absolute temperature T. Consider R as universal gas constant. The pressure of the mixture of gases is ______.
Cooking gas containers are kept in a lorry moving with uniform speed. The temperature of the gas molecules inside will ______.
