Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
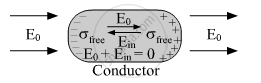
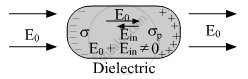
Explain briefly, using a proper diagram, the difference in the behavior of a conductor and a dielectric in the presence of an external electric field.
उत्तर
When a conductor is placed in an external electric field, the free charges present inside the conductor rearrange themselves in such a manner that the electric field due to induced charges opposes the external field within the conductor. After some time a static situation is achieved when the two fields cancel each other and the net electrostatic field in the conductor becomes zero.
Dielectrics are non-conducting in nature, i.e. they have no free charge carriers. Thus, in a dielectric, free movement of charges is not possible. In Dielectrics the external field induces dipole moment by stretching molecules of the dielectric. The collective effect of all the molecular dipole moments creates the net charge on the surface of the dielectric which produces a field that opposes the external field. However, the opposing field does not exactly cancel the external field but just reduces its value. So-net electrostatic field in a dielectric is non-zero.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Distinguish with the help of a suitable diagram, the difference in the behaviour of a conductor and a dielectric placed in an external electric field.
How does polarised dielectric modify the original external field?
Define the terms polarization of a dielectric and write its relation with susceptibility.
Two metal plates having charges Q, −Q face each other at some separation and are dipped into an oil tank. If the oil is pumped out, the electric field between the plates will
A dielectric slab is inserted between the plates of a capacitor. The charge on the capacitor is Q and the magnitude of the induced charge on each surface of the dielectric is Q'.
Define the term polarization of a dielectric and write the expression for a linear isotropic dielectric in terms of electric field.
The dielectric constant of a medium is also known as ______
The voltage rating of a parallel plate capacitor is 500V. Its dielectric can withstand a maximum electric field of 106 V/m. The plate area is 10-4 m2. What is the dielectric constant if the capacitance is 15 pF?
(given ε0 = 8.86 × 10-12 C2/Nm2)
An isolated parallel plate capacitor is maintained at a certain potential difference. When a 3 mm thick slab is introduced between the plates, in order to maintain the same potential difference the distance between the plates is increased by 2.4 mm. The dielectric constant of the slab will be ______.
