Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Explain how spectrum is formed.
उत्तर
When white light passes through a glass prism, it spreads out into a band of different colours called the spectrum of light.
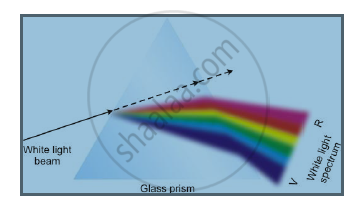
- When white light is dispersed into seven colours by a glass prism, different colours bend through different angles with respect to the incident ray.
- The sequence of colours given by the prism is Violet, Indigo, Blue, Green, Yellow, Orange and Red.
- Of the seven colours, red light bends the least, while violet light bends the most. So, the rays of each colour emerge along different paths and appear distinct. Hence, we get a spectrum of seven different colours.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
In your laboratory you trace the path of light rays through a glass slab for different values of angle of incidence (∠i) and in each case measure the values of the corresponding angle of refraction (∠r) and angle of emergence (∠e). On the basis of your observations your correct conclusion is:
(a) ∠i is more than ∠r, but nearly equal to ∠e
(b) ∠i is less then ∠r, but nearly equal to ∠e
(c) ∠i is more than ∠e, but nearly equal to ∠r
(d) ∠i is less than ∠e, but nearly equal to ∠r
Four students P, Q, R and S traced the path of a ray of light passing through a glass slab for an angle of incidence 40° and measured the angle of refraction. The values as measured them were 18°; 22°; 25° and 30° respectively. The student who has performed the experiment methodically is
(A) P
(B) Q
(C) R
(D) S
Write a relationship between the angle of incidence and angle of refractions for a given pair of media
A ray of light passes from water to air. How does the speed of light change?
Light passes through a rectangular glass slab and through a triangular glass prism. In what way does the direction of the two emergent beams differ and why?
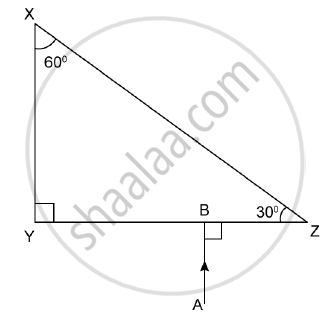
The following diagram shows a 60°, 30°, 90° glass prism of critical angle 42°, Copy the diagram and complete the path of incident ray AB emerging out of the prism marking the angle of incidence on each surface.
A ray of light passes from glass into air. The angle of refraction will be:
(a) equal to the angle of incidence
(b) greater than the angle of incidence
(c) smaller than the angle of incidence
(d) 45°
How can you bend light away from the normal?
Draw diagrams to show the refraction of light from glass to air. In diagram, label the incident ray, refracted ray, the angle of incidence (i) and the angle of refraction (r).
How is the refractive index of a medium related to the speed of light in it?
For which colour of white light, is the refractive index of a transparent medium the most?
A ray of light strikes the surface of a rectangular glass block such that the angle of incidence in
air is 0°.
In each case, draw diagram to show the path taken by the ray as it passes through the glass block and emerges from it.
How does the speed of light change when it passes from glass to water?
The diagram alongside shows the refraction of a ray of light from air to a liquid.
- Write the values of (i) angle of incidence, (ii) angle of refraction.
- Use Snell’s law to find the refractive index of liquid with respect to air.

An object is viewed through a glass prism with its vertex pointing upwards. It appears to be displaced upward. Explain the reason.
A ray of light enters a glass slab ABDC as shown in figure and strikes at the centre O of the circular part AC of the slab. The critical angle of glass is 42°. Complete the path of the ray till it emerges out from the slab. Mark the angles in the diagram wherever necessary.

Select from the following the best experimental set-up for tracing the path of a ray of light through a glass slab: (A) I
(A) I
(B) II
(C) III
(D) IV
Select from the following the best set-up for tracing the path of a ray of light through a rectangular glass slab:
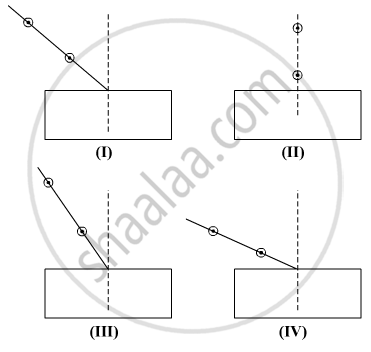
(A) I
(B) II
(C) III
(D) IV
(i) What is the relation between the refractive index of water with respect to air `("_aμ_\text(w))` and the refractive index of air with respect to water `("_\text(w)μ_ a)` .
(ii) If the refractive index of water with respect to air `("_aμ_\text(w))` is`5/3`. Calculate the refractive index of air with respect to water `("_\text(w)μ_ a)` .
Define the term refractive index of a medium. What do you understand by the statement 'the refractive index of glass is 1.5 for white light'?
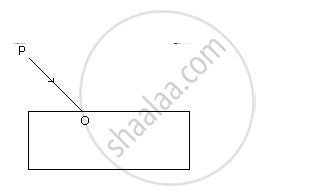
In the fig., PO is a ray of light incident on a rectangular glass block.
(a) Complete the path of the ray through the block.
(b) In the diagram, mark the angle of incidence (i) and the angle of refraction (r) at the first interface. How is the refractive index of glass related to the angles I and r?
(c) Mark angle of emergence by the letter e. How are the angles i and e related?
(d) Which two rays are parallel to each other? Name them.
(e) Indicate in the diagram the lateral displacement between the emergent ray and the incident ray.
Make the correct for each of the following :
With reference to the fig, the refractive index of the glass block is
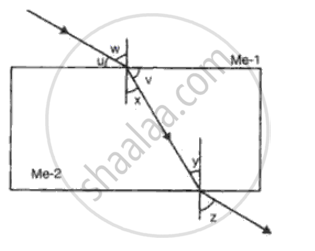
A ray of light strikes the surface at a rectangular glass slab such that the angle of incidence is 45o.
In each case, draw diagram to show the path taken by the ray as it passes through the glass slab and emerges from it.
How does the deviation produced by a prism depend on the refraction index of its material.
What is meant by the refraction of light?
Why is the colour red used as a sign of danger?
What is the refractive index of water
How does the angle of deviation produced by a prism depend on the colour of light used? Which colour of white light is deviated (i) most, (ii) least, by a prism?
What do you understand by the deviation produced by a prism?
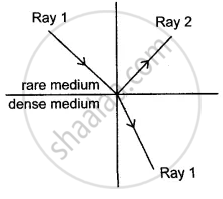
A ray of light moves from a rare medium to a dense medium as shown in the diagram below. Write down the number of the ray which represents the partially reflected ray.
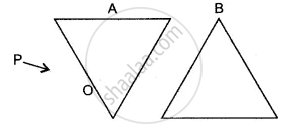
The figure shows two prisms A and B. A monochromatic ray of light PO is incident at the face of the prism A. Complete the diagram to show the path of the ray till it emerges out of the prism B.
Light passes through a rectangular glass slab and through a triangular glass prism. In what way does the direction of the two emergent beams differ and why?
A ray of monochromatic light is incident from the air on a glass slab:
(i) Draw a labelled ray diagram showing the change in the path of the ray till it emerges from the glass slab.
(ii) Name the two rays that are parallel to each other.
(iii) Mark the lateral displacement in your diagram.
The diagram shows the path of a ray of light through a rectangular glass block placed in a liquid of uniform density.

What is the angular, deviation of the emergent ray from the glass block with respect to the incident ray?
A ray of light PQ is incident normally on the hypotenuse of a right-angled prism ABC as shown in the diagram given below:
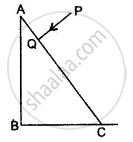
(i) Copy the diagram and complete the path of the ray PQ till it emerges from the prism.
(ii) What is the value of the angle of deviation of the ray?
(iii) Name an instrument where this action of the prism is used.
The speed of light in air is 3 × 108 ms-1. Calculate the speed of light in water. The refractive index of water is 4/3.
A ray of light strikes the surface of a rectangular glass slab such that the angle of incidence in air is
- 0°,
- 45°.
In each case, draw a diagram to show the path taken by the ray as it passes through the glass slab and emerges from it.
