Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Explain how spectrum is formed.
Solution
When white light passes through a glass prism, it spreads out into a band of different colours called the spectrum of light.
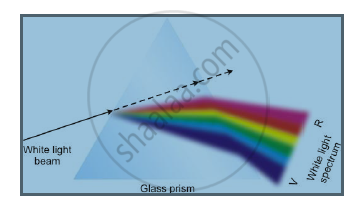
- When white light is dispersed into seven colours by a glass prism, different colours bend through different angles with respect to the incident ray.
- The sequence of colours given by the prism is Violet, Indigo, Blue, Green, Yellow, Orange and Red.
- Of the seven colours, red light bends the least, while violet light bends the most. So, the rays of each colour emerge along different paths and appear distinct. Hence, we get a spectrum of seven different colours.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
When rays of light are incident on a glass slab then the incident ray and emergent ray are _________ each other.
- perpendicular
- parallel
- opposite
- concurrent
Write a short note on dispersion of light.
A student traces the path of a ray of light through a rectangular glass slab for the different values of angle of incidence. He observes all possible precautions at each step of the experiment. At the end of the experiment, on analyzing the measurements, which of the following conclusions is he likely to draw?
(A) ∠i = ∠e < ∠r
(B) ∠i < ∠e < ∠r
(C) ∠i > ∠e > ∠r
(D) ∠i = ∠e > ∠r
After tracing the path of a ray of light passing through a rectangular glass slab for four different values of the angle of incidence, a student reported his observations in tabular form as given below:
| S.No | ∠ i | ∠ r | ∠ e |
| I | 30° | 19° | 29° |
| II | 40° | 28° | 40° |
| III | 50° | 36° | 50° |
| IV | 60° | 40° | 59° |
The best observation is
(A) I
(B) II
(C) III
(D) IV
The speed of light in glass is 2 × 105 km/s. What is the refractive index of glass?
A ray of light passes from water to air. How does the speed of light change?
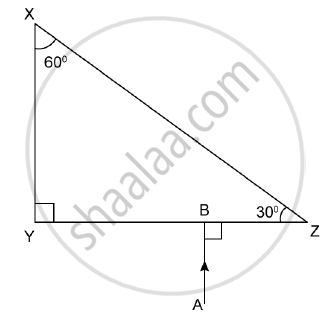
The following diagram shows a 60°, 30°, 90° glass prism of critical angle 42°, Copy the diagram and complete the path of incident ray AB emerging out of the prism marking the angle of incidence on each surface.
How is the reflection of light ray from a plane mirror different from the refraction of light ray as it enters a block of glass?
A monochromatic ray of light passes from air to glass. The wavelength of light in air is λ, the speed of light in air is c and in glass is V. If the absolute refractive index of glass is 1.5, write down
- the relationship between c and V,
- the wavelength of light in glass.
For which colour of white light, is the refractive index of a transparent medium the most?
Light of a single colour is passed through a liquid having a piece of glass suspended in it. On changing the temperature of liquid, at a particular temperature the glass piece is not seen. When is the glass piece not seen?
When light travels from a rarer to a denser medium, its speed ______.
The highest refractive index is of ______.
With the help of diagram of the principal section of a prism, indicate its refracting surfaces, refracting edge and base.
How does the speed of light change when it passes from glass to water?
Fill in the blanks to complete the following sentence
The refractive index of glass with respect to air is 3/2. The refractive index of air with respect to glass will be ……………….
An object is viewed through a glass prism with its vertex pointing upwards. It appears to be displaced upward. Explain the reason.
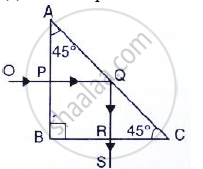
A ray of light OP passes through a right angles prism as shown in the adjacent diagram.
(a) State the angles of incidence at the faces AC and BC.
(b) Name the phenomenon which the ray suffers at the face AC.
A total reflecting right angled isosceles prism can be used to deviate a ray of light through:
(a) 30° (b) 60° (c) 75° (d) 90°.
Trace the path of a ray of light incident at an angle of 45° on a rectangular glass slab. Write the measure of the angle of refraction, the angle of emergence and the lateral displacement suffered by the ray as it passes through the slab.
A ray of light falls normally on the surface of a transparent glass slab. Draw a ray diagram to show its path and also mark angle of incidence and angle of emergence.
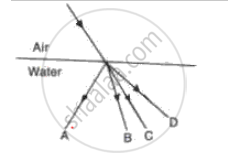
A ray of light passes from air to water. In fig. 39, which of the ray A, B, C and D is the correct refracted ray?
Which of the following has the highest refractive index:
Fill in the blank to complete the following sentence:
When light travels from a rarer to a denser medium, it bends ...........
Which colour of light travels fastest in any medium except air?
A ray of light strikes the surface at a rectangular glass slab such that the angle of incidence is 45o.
In each case, draw diagram to show the path taken by the ray as it passes through the glass slab and emerges from it.
What is meant by the refraction of light?
Define the term refractive index of a medium in terms of velocity of light.
The refractive index of air with respect to glass is defined: as gµa = sin i/sin r
Write down a similar expression for aµg in terms of angle i and r.
How does the angle of deviation produced by a prism depend on the angle of incidence of light at the prism surface? Draw a graph to illustrate your answer.
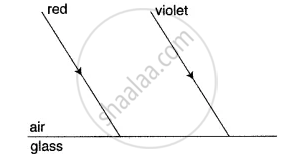
Two parallel rays of Red and Violet travelling through the air, meet the air-glass boundary as shown in the above figure. Will their paths inside the glass be parallel? Give a reason for your answer.
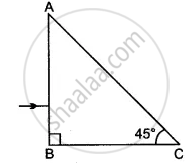
Trace a ray of light incident at 30° on a surface if travelling from glass to air. What is the angle of refraction in this case? (R.I. for glass = 3/2).
Explain with the help of a diagram of how fish is able to see the objects above it.
Calculate the velocity of light in a glass block of refractive index 1.5. (Velocity of light in air = 3 × 108 m/s)
A ray of light PQ is incident normally on the hypotenuse of a right-angled prism ABC as shown in the diagram given below:
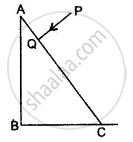
(i) Copy the diagram and complete the path of the ray PQ till it emerges from the prism.
(ii) What is the value of the angle of deviation of the ray?
(iii) Name an instrument where this action of the prism is used.
The refractive index of glass with respect to air is 3/2. What is the refractive index of air with respect to glass?
The diagram below shows two parallel rays A (Orange) & B (Blue) incident from air, on air-glass boundary.
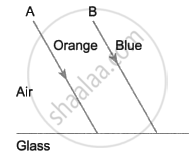
- Copy and complete the path of the rays A and B.
- How do the speeds of these rays differ in glass?
- Are the two refracted rays in glass parallel? Give a reason.
