Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
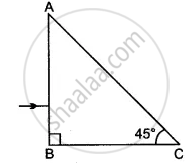
Explain how spectrum is formed.
उत्तर
When white light passes through a glass prism, it spreads out into a band of different colours called the spectrum of light.
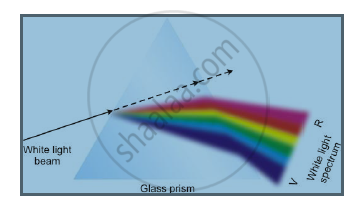
- When white light is dispersed into seven colours by a glass prism, different colours bend through different angles with respect to the incident ray.
- The sequence of colours given by the prism is Violet, Indigo, Blue, Green, Yellow, Orange and Red.
- Of the seven colours, red light bends the least, while violet light bends the most. So, the rays of each colour emerge along different paths and appear distinct. Hence, we get a spectrum of seven different colours.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
State the dependence of angle of deviation On the wavelength of light
A ray of light passes from water to air. How does the speed of light change?
Which of the above wavelengths has a higher frequency?
For which colour of white light, is the refractive index of a transparent medium the most?
A ray of light strikes the surface of a rectangular glass block such that the angle of incidence in
air is 0°.
In each case, draw diagram to show the path taken by the ray as it passes through the glass block and emerges from it.
With the help of diagram of the principal section of a prism, indicate its refracting surfaces, refracting edge and base.
How does the angle of minimum deviation produces by a prism change with increase in :
the wavelength of incident light
A coin is places at the bottom of a beaker containing water (refractive index = 4/3) to a depth of 12 cm. By what height the coin appears to be raised when seen from vertically above?
The refractive index of glass is 1.5. From a point P inside a glass block, draw rays PA, PB and PC incident on the glass air surface at an angle of incidence 30°, 42° and 60° respectively.
- In the diagram show the approximate direction of these rays as they emerge out of the block.
- What is the angle of refraction for the ray PB?
`("Take" sin 42° =2/3)`
Select from the following the best experimental set-up for tracing the path of a ray of light through a glass slab: (A) I
(A) I
(B) II
(C) III
(D) IV
Trace the path of a ray of light incident at an angle of 45° on a rectangular glass slab. Write the measure of the angle of refraction, the angle of emergence and the lateral displacement suffered by the ray as it passes through the slab.
Four students showed the following traces of the path of a ray of light passing through a rectangular glass slab.
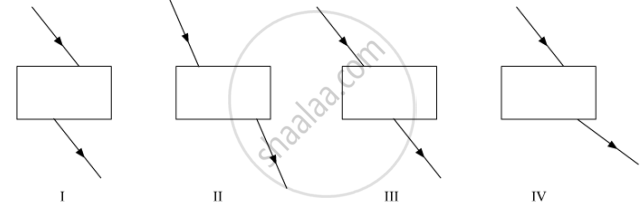
The trace most likely to be correct is that of student
(A) I
(B) II
(C) III
(D) IV
Fig shows a lens as a combination of a glass block and two prisms.
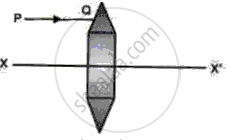
(i) Name the lens formed by the combination.
(ii) what is the XX' called?
(iii) Complete the ray diagram and show the path of the incident ray PQ after passing through the lens.
(iv) The final emergent ray will either meet XX' at a point or appear to come from a point on XX'. what is the point called?
Fig shows a lens as a combination of a glass block and two prisms.
(i) Name the lens formed by the combination.
(ii) What is the line XX' called?
(iii) Complete the path of the incident ray PQ after passing through the lens.
(iv) The final emergent ray either meets XX' at a point or appears to come from a point on XX'. Label it as F, What is this point called?
In an experiment of finding the refractive index of glass, if blue light is replaced by the red light, how will the refractive index of glass change? Give reason in support of your answer.
Light of a single colour is passed through a liquid having a piece of glass suspended in it. On changing the temperature of liquid, at a particular temperature, the glass piece is not seen.
Why is the light of a single colour used ?
The critical angle for glass-air interface is :
Name the phenomenon responsible in the following case:
Twinkling of stars
Glass is transparent in nature. Why does glass powder look opaque? When water is poured over it, it again becomes transparent. Why?
A ray of light passes from water to air. How does the speed of light change?
Name one main factor on which the direction of bending of a ray of light depends.
Express the refractive index μ of a medium in terms of the velocity of light.
In what condition a prism is said to be in the position of minimum deviation? What is the direction of the refracted ray inside the prism in this condition?
What do you understand by the deviation produced by a prism?
A ray of monochromatic light is incident from air into a glass slab. Draw a labelled ray diagram indicating the change in its path till it emerges out of the slab. In the diagram, mark the angle of incidence (i) and the angle of refraction (r) at the first interface. How is the refractive index of glass related to the angles i and r?
After a robbery, if a window has been broken, there will be tiny particles of glass. Some of these will be found at the scene of the crime and some may be caught in the thief’s clothing. If the police can prove that these particles are identical, they have a strong case.
A method of doing this is to suspend the particles of glass in a special liquid. Light of a single colour is thrown through the liquid and the particles viewed through a microscope. The temperature of the liquid is then slowly altered. This alters the speed of light through the liquid (i.e., it alters the refractive index). At one particular temperature, the particles of glass disappear. It this happens at the same temperature for both sets of glass particles, they probably came from the same broken pane of glass.
Complete and copy the diagram to show how light bends when it travels from the liquid to the glass and back to the liquid, If the light slows down in the glass.
Draw a diagram to show the refraction of a monochromatic light ray through an equilateral prism. On the diagram, label the incident, refracted, and emergent rays. It also indicates the angle of deviation by the letter δ.
How does the angle of deviation produced by a prism depend on the angle of incidence of light at the prism surface? Draw a graph to illustrate your answer.
How will you verify the laws of refraction or how the refractive index of glass is determined in the laboratory?
The diagram shows the path of a ray of light through a rectangular glass block placed in a liquid of uniform density.

(a) Does the light speed up or slow down in the glass,
(b) Give the reason for your answer.
The diagram shows the path of a ray of light through a rectangular glass block placed in a liquid of uniform density.

What is the angular, deviation of the emergent ray from the glass block with respect to the incident ray?
Calculate the velocity of light in a glass block of refractive index 1.5. (Velocity of light in air = 3 × 108 m/s)