Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Explain in detail the isothermal process.
उत्तर
Isothermal process: It is a process in which the temperature remains constant but the pressure and volume of a thermodynamic system will change. The ideal gas equation is
PV = µRT
Here, T is constant for this process So the equation of state for the isothermal process is given by
PV = Constant ..................…(1)
This implies that if the gas goes from one equilibrium state (P1, V1) to another equilibrium state (P2, V2) the following relation holds for this process
P1V1 = P2V2 ….............(2)
Since PV = constant, P is inversely proportional to `"V" ("P" ∝ 1/"V")`. This implies that the PV graph is a hyperbola. The pressure-volume graph for constant temperature is also called isotherm. We know that for an ideal gas the internal energy is a function of temperature only. For an isothermal process since the temperature is constant, the internal energy is also constant. This implies that dU or ∆U = 0.
For an isothermal process, the first law of thermodynamics can be written as,
Q = W …...........(3)

(a) Quasi-static isothermal expansion (b) Quasi-static isothermal compression

Isothermal expansion and isothermal compression
From equation (3), we infer that the heat supplied to gas is used to do only external work. It is a common misconception that when there is a flow of heat to the system, the temperature will increase. For the isothermal process, this is not true. The isothermal compression takes place when the piston of the cylinder is pushed. This will increase the internal energy which will flow out of the system through thermal contact.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Explain the cyclic process.
An ideal gas of volume 2 L is adiabatically compressed to (1/10)th of its initial volume. Its initial pressure is 1.01 x 105 Pa, calculate the final pressure. (Given 𝛾 = 1.4)
Explain graphically (i) positive work with varying pressure, (ii) negative work with varying pressure, and (iii) positive work at constant pressure.
Explain work done during a thermodynamic process.
The V-T diagram of an ideal gas which goes through a reversible cycle A→B→C→D is shown below. (Processes D→A and B→C are adiabatic)
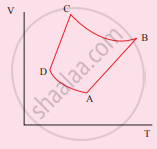
The corresponding PV diagram for the process is (all figures are schematic)
Give the equation of state for an adiabatic process.
Ideal gas for which 'ϒ' = 1.5 is suddenly compressed to `1/4`th of its initial volume. The ratio of 4 the final pressure to the initial pressure is ______.
`(ϒ = "C"_"p"/"C"_"v")`
Which of the following processes is reversible?
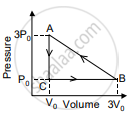
In the figure shown here, the work done in the process ACBA is ______.
In a certain thermodynamical process, the pressure of a gas depends on its volume as kV3. The work done when the temperature changes from 100°C to 300°C will be ______ nR, where n denotes number of moles of a gas.
