Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Explain the cyclic process.
Explain cyclic process with the help of neat and labelled p-V diagram.
उत्तर
- A thermodynamic process that returns a system to its initial state is a cyclic process.
- In this process, the initial and the final state is the same.
- For a cyclic process, the total change in the internal energy of a system is zero. (ΔU = 0).
- According to the first law of thermodynamics, we have, for a cyclic process, Q = W
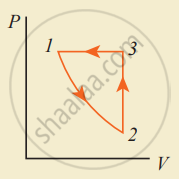
- The given figure shows the p-V diagram of a cyclic process which is a closed-loop.

p-V diagram of cyclic process - Working of all heat engines is a cyclic process.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Explain why The climate of a harbour town is more temperate than that of a town in a desert at the same latitude.
Give an example of some familiar process in which heat is added to an object, without changing its temperature.
An ideal gas is taken through an isothermal process. If it does 2000 J of work on its environment, how much heat is added to it?
For work done to be reversible, the process should be ______
What is a thermodynamic process?
Explain graphically (i) positive work with varying pressure, (ii) negative work with varying pressure, and (iii) positive work at constant pressure.
Explain work done during a thermodynamic process.
Explain the thermodynamics of the isobaric process.
Explain thermodynamics of the adiabatic process.
When a cycle tyre suddenly bursts, the air inside the tyre expands. This process is ____________.
When food is cooked in a vessel by keeping the lid closed, after some time the steam pushes the lid outward. By considering the steam as a thermodynamic system, then in the cooking process
Apply first law for an isothermal process.
Give the equation of state for an adiabatic process.
Explain in detail an adiabatic process.
Explain in detail the isochoric process.
What are the limitations of the first law of thermodynamics?
In a petrol engine, (internal combustion engine) air at atmospheric pressure and temperature of 20°C is compressed in the cylinder by the piston to `1/8` of its original volume. Calculate the temperature of the compressed air. (For air γ = 1.4)
Consider the following cyclic process consist of isotherm, isochoric and isobar which is given in the figure.
Draw the same cyclic process qualitatively in the V-T diagram where T is taken along the x-direction and V is taken along the y-direction. Analyze the nature of heat exchange in each process.
An ideal gas is made to go from a state A to stale B in the given two different ways (see figure) (i) an isobaric and then an isochoric process and (ii) an isochoric and then an isobaric process. The work done by gas in the two processes are W1 and W2 respectively. Then,

One mole of an ideal gas with `gamma` = 1.4 is adiabatically compressed so that its temperature rises from 27° C to 47° C. The change in the internal energy of the gas is (R = 8.3 J/mol.K) ____________.
Two identical samples of a gas are allowed to expand (i) isothermally (ii) adiabatically. Work done is ____________.
In which of the following processes, beat is neither absorbed nor released by a system?
An ideal gas is compressed to half its initial volume by means of several processes. Which of the process results in the maximum work done on the gas?
In a certain thermodynamical process, the pressure of a gas depends on its volume as kV3. The work done when the temperature changes from 100°C to 300°C will be ______ nR, where n denotes number of moles of a gas.
An ideal gas is taken through a cyclic process ABCDA as shown in figure. The net work done by the gas during the cycle is ______.
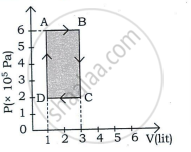
In a cyclic process, if ΔU = internal energy, W = work done, Q = Heat supplied then ______.
