Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Explain thermodynamics of the adiabatic process.
उत्तर
- An adiabatic process is a process during which there is no transfer of heat from or to the system.
- For adiabatic change, Q = 0.
∴ ΔU + W = 0
∴ ΔU = –W - This implies, for adiabatic expansion, W is positive and ΔU is negative i.e. when work is done by the system adiabatically its internal energy decreases.
- Similarly, when a system is compressed adiabatically, W is negative and ΔU is positive i.e., the internal energy of the system increases in an adiabatic compression.
- Heat transfer to and from the system is prevented by either perfectly insulating the system from its environment or by carrying out the change rapidly so that there is no time for any exchange of heat.
- The temperature of the system changes, i.e., ΔT ≠ 0
- Usually, it is a sudden change and the system does not find any time to exchange heat with its environment.
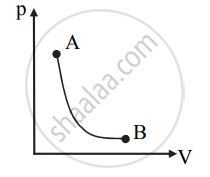
- p-V diagram for the adiabatic process is as shown below:
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Explain why The climate of a harbour town is more temperate than that of a town in a desert at the same latitude.
Heating a gas in a constant volume container is an example of which process?
What is a thermodynamic process?
Draw a p-V diagram of the reversible process.
Draw a p-V diagram of the irreversible process.
Draw a p-V diagram showing positive work at constant pressure.
Explain work done during a thermodynamic process.
When a cycle tyre suddenly bursts, the air inside the tyre expands. This process is ____________.
Give the equation of state for an isothermal process.
Give an expression for work done in an isothermal process.
Apply first law for an isothermal process.
Give an equation state for an isochoric process.
What is meant by a reversible and irreversible processes?
Explain the isobaric process and derive the work done in this process.
An ideal gas is expanded isothermally from volume V1 to volume V2 and then compressed adiabatically to original volume V1. If the initial pressure is P1, the final pressure is P3 and net work done is W, then ____________.
An ideal gas is made to go from a state A to stale B in the given two different ways (see figure) (i) an isobaric and then an isochoric process and (ii) an isochoric and then an isobaric process. The work done by gas in the two processes are W1 and W2 respectively. Then,

An ideal gas A and a real gas B have their volumes increased from V to 2V under isothermal conditions. The increase in internal energy ____________.
In an isothermal process, the volume of an ideal gas is halved. One can say that ____________.
An ideal gas is compressed to half its initial volume by means of several processes. Which of the process results in the maximum work done on the gas?
We consider a thermodynamic system. If `Delta"U"` represents the increase in its internal energy and W the work done by the system, which of the following statements is true?
The work done on the system in changing the state of a gas adiabatically from equilibrium state A to equilibrium state B is 22.4 J. If the gas is taken from state A to B through another process in which the net heat absorbed by the system is 15.5 cal, then the net work done by the system in the latter case is ______.
( l cal = 4.2 J)
Which of the following processes is reversible?
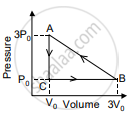
In the figure shown here, the work done in the process ACBA is ______.
In a certain thermodynamical process, the pressure of a gas depends on its volume as kV3. The work done when the temperature changes from 100°C to 300°C will be ______ nR, where n denotes number of moles of a gas.
When an inflated ballon is suddenly burst, why is the emerging air slightly cooled?
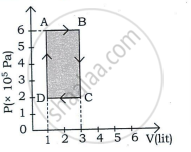
An ideal gas is taken through a cyclic process ABCDA as shown in figure. The net work done by the gas during the cycle is ______.
Explain how can a gas be expanded at constant temperature.
