Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Explain the isobaric process and derive the work done in this process.
उत्तर
Isobaric process: This is a thermodynamic process that occurs at constant pressure. Even though the pressure is constant in this process, temperature, volume and internal energy are not constant. From the ideal gas equation, we have
V = `((μ"R")/"P")"T"` .........(1)
Here, `(μ"R")/"P"` = constant
In an isobaric process the temperature is directly proportional to volume.
V ∝ T (Isobaric process) …........(2)
This implies that for an isobaric process, the V-T graph is a straight line passing through the origin.
If gas goes from a state (Vi, Ti) to (Vf, Tf) at constant pressure, then the system satisfies the following equation
`"T"_"f"/"V"_"f" = "T"_"i"/"V"_"i"` ...........(3)
Examples for Isobaric process:
(i) When the gas is heated and pushes the piston so that it exerts a force equivalent to atmospheric pressure plus the force due to gravity then this process is isobaric.
(ii) Most of the cooking processes in our kitchen are isobaric processes. When the food is cooked in an open vessel, the pressure above the food is always at atmospheric pressure. The PV diagram for an isobaric process is a horizontal line parallel to the volume axis. Figure (a) represents the isobaric process where volume decreases figure
(b) represents the isobaric process where volume increases.

PV diagram for an isobaric process
The work done in an isobaric process: Work done by the gas
W = `int_("V"_"i")^("V"_"f") "PdV"` ..........(4)
In an isobaric process, the pressure is constant, so P comes out of the integral,
W = `"P" int_("V"_"i")^("V"_"f") "dV"` ........(5)
W = P[Vf – Vi] = PΔV ........(6)
Where ∆V denotes the change in the volume. If ∆V is negative, W is also negative. This implies that the work is done on the gas. If ∆V is positive, W is also positive, implying that work is done by the gas equation.
The equation (6) can also be rewritten using the ideal gas equation.
From ideal gas equation
PV = μRT and V = `(μ"RT")/"P"`
Substituting this in equation (6) we get
W = `μ"RT"_"f" (1 - "T"_"i"/"T"_"f")` ...........(7)
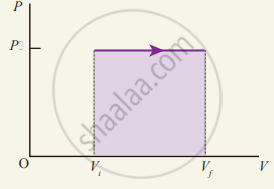
Work done in an isobaric process
In the PV diagram, the area under the isobaric curve is equal to the work done in the isobaric process. The shaded area in the above diagram is equal to the work done by the gas.
The first law of thermodynamics for the isobaric process is given by
ΔU = Q − PΔV ......(8)
W = PΔV, ΔU = `"Q" - μ"RT"_"f" [1 - "T"_"i"/"T"_"f"]`
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Give an example of some familiar process in which heat is added to an object, without changing its temperature.
Draw a p-V diagram of the reversible process.
Draw a p-V diagram of the irreversible process.
Differentiate between the reversible and irreversible processes.
Write a note on free expansion.
Apply first law for an adiabatic process.
Give the equation of state for an adiabatic process.
Give an equation state for an isochoric process.
Derive the work done in an adiabatic process.
Give any two types of a thermodynamic process.
