Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Explain thermodynamics of the adiabatic process.
उत्तर
- An adiabatic process is a process during which there is no transfer of heat from or to the system.
- For adiabatic change, Q = 0.
∴ ΔU + W = 0
∴ ΔU = –W - This implies, for adiabatic expansion, W is positive and ΔU is negative i.e. when work is done by the system adiabatically its internal energy decreases.
- Similarly, when a system is compressed adiabatically, W is negative and ΔU is positive i.e., the internal energy of the system increases in an adiabatic compression.
- Heat transfer to and from the system is prevented by either perfectly insulating the system from its environment or by carrying out the change rapidly so that there is no time for any exchange of heat.
- The temperature of the system changes, i.e., ΔT ≠ 0
- Usually, it is a sudden change and the system does not find any time to exchange heat with its environment.
- p-V diagram for the adiabatic process is as shown below:
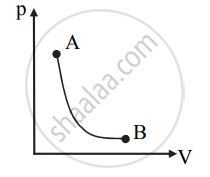
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A thermodynamic system is taken from an original state to an intermediate state by the linear process shown in Figure

Its volume is then reduced to the original value from E to F by an isobaric process. Calculate the total work done by the gas from D to E to F
What is a thermodynamic process?
Draw a p-V diagram showing positive work at constant pressure.
Explain the cyclic process.
When you exercise in the morning, by considering your body as a thermodynamic system, which of the following is true?
Apply first law for an isobaric process.
What is a cyclic process?
Explain the isobaric process and derive the work done in this process.
Explain in detail the isochoric process.
What are the limitations of the first law of thermodynamics?
Draw the TP diagram (P-x axis, T-y axis), VT(T-x axis, V-y axis) diagram for
- Isochoric process
- Isothermal process
- Isobaric process
In an adiabatic expansion of the air, the volume is increased by 4%, what is the percentage change in pressure? (For air γ = 1.4)
Consider the following cyclic process consist of isotherm, isochoric and isobar which is given in the figure.
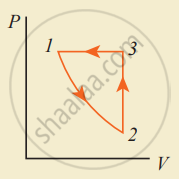
Draw the same cyclic process qualitatively in the V-T diagram where T is taken along the x-direction and V is taken along the y-direction. Analyze the nature of heat exchange in each process.
For a given ideal gas 6 × 105 J heat energy is supplied and the volume of gas is increased from 4 m3 to 6 m3 at atmospheric pressure. Calculate
- the work done by the gas
- change in internal energy of the gas
- graph this process in PV and TV diagram
An ideal gas is expanded isothermally from volume V1 to volume V2 and then compressed adiabatically to original volume V1. If the initial pressure is P1, the final pressure is P3 and net work done is W, then ____________.
An ideal gas is made to go from a state A to stale B in the given two different ways (see figure) (i) an isobaric and then an isochoric process and (ii) an isochoric and then an isobaric process. The work done by gas in the two processes are W1 and W2 respectively. Then,

In which of the following processes, beat is neither absorbed nor released by a system?
In an isothermal process, the volume of an ideal gas is halved. One can say that ____________.
Assertion: Equal volumes of monatomic and polyatomic gases are adiabatically compressed separately to equal compression ratio `("P"_2/"P"_1)`. Then monatomic gas will have greater final volume.
Reason: Among ideal gases, molecules of a monatomic gas have the smallest number of degrees of freedom.
An ideal gas is compressed to half its initial volume by means of several processes. Which of the process results in the maximum work done on the gas?
Ideal gas for which 'ϒ' = 1.5 is suddenly compressed to `1/4`th of its initial volume. The ratio of 4 the final pressure to the initial pressure is ______.
`(ϒ = "C"_"p"/"C"_"v")`
The work done on the system in changing the state of a gas adiabatically from equilibrium state A to equilibrium state B is 22.4 J. If the gas is taken from state A to B through another process in which the net heat absorbed by the system is 15.5 cal, then the net work done by the system in the latter case is ______.
( l cal = 4.2 J)
Give any two types of a thermodynamic process.
Explain the thermodynamic process.
