Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Explain the thermodynamics of the isochoric process.
उत्तर
- A thermodynamic process in which the volume of the system is kept constant is called the isochoric process.
- A system does no work in its environment during an isochoric process.
- For an isochoric process, ΔV = 0, and from the first law of thermodynamics, ΔU = Q.
- The temperature of the system changes, i.e., ΔT ≠ 0.
- This means that for an isochoric change, all the energy added in the form of heat remains in the system itself and causes an increase in its internal energy. Also, as volume is unchanged, no work is done.
- The first law of thermodynamics for the isochoric process is, Q = ΔU ….(1)
The change in internal energy is given by,
ΔU = nCVΔT ….(2)
The work done is given by,
W = pΔV = 0 ….(∵ ΔV = 0)
From equations (1) and (2),
The heat exchanged is given by,
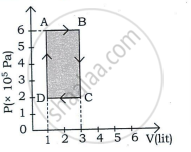
Q = ΔU = nCVΔT - p-V diagram of isochoric process is as shown below:

संबंधित प्रश्न
Explain why The climate of a harbour town is more temperate than that of a town in a desert at the same latitude.
Give an example of some familiar process in which heat is added to an object, without changing its temperature.
Heating a gas in a constant volume container is an example of which process?
What is a thermodynamic process?
Draw a p-V diagram showing positive work with varying pressure.
Draw a p-V diagram showing positive work at constant pressure.
Differentiate between the reversible and irreversible processes.
Explain the cyclic process.
Explain graphically (i) positive work with varying pressure, (ii) negative work with varying pressure, and (iii) positive work at constant pressure.
Apply first law for an isothermal process.
Apply first law for an adiabatic process.
Give the equation of state for an adiabatic process.
Give an equation state for an isochoric process.
Draw the PV diagram for the isochoric process.
Derive the work done in an adiabatic process.
Explain in detail the isochoric process.
What are the limitations of the first law of thermodynamics?
An ideal gas is taken in a cyclic process as shown in the figure. Calculate
- work done by the gas
- work done on the gas
- Net work done in the process

Among the amount of heat absorbed and the amount of work done by a system, ______
In which of the following processes, beat is neither absorbed nor released by a system?
An ideal gas A and a real gas B have their volumes increased from V to 2V under isothermal conditions. The increase in internal energy ____________.
In an isothermal process, the volume of an ideal gas is halved. One can say that ____________.
We consider a thermodynamic system. If `Delta"U"` represents the increase in its internal energy and W the work done by the system, which of the following statements is true?
In a certain thermodynamical process, the pressure of a gas depends on its volume as kV3. The work done when the temperature changes from 100°C to 300°C will be ______ nR, where n denotes number of moles of a gas.
An ideal gas is taken through a cyclic process ABCDA as shown in figure. The net work done by the gas during the cycle is ______.
Explain how can a gas be expanded at constant temperature.
