Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Explain the thermodynamics of the isobaric process.
उत्तर
- A thermodynamic process that is carried out at constant pressure i.e., Δp = 0 is called the isobaric process.
- For an isobaric process, none of the quantities ΔU, Q, and W is zero.
- The temperature of the system changes, i.e., ΔT ≠ 0.
- The energy exchanged is used to do work as well as to change internal energy causing an increase in temperature. Thus, Q = ΔU + W.
- As work is done volume changes during the process.
- Heat exchanged in case of an isobaric process:
a. Consider an ideal gas undergoing volume expansion at constant pressure.
b. If Vi and Ti are its volume and temperature in the initial state of a system and Vf and Tf are its final volume and temperature respectively, the work done in the expansion is given by,
W = pdV = p(Vf – Vi) = nR(Tf – Ti) ….(1)
c. Also, the change in the internal energy of a system is given by, ΔU = nCVΔT = nCV(Tf – Ti) ….(2)
Where, CV is the specific heat at constant volume, and ΔT = (Tf – Ti) is the change in its temperature during the isobaric process.
d. According to the first law of thermodynamics, the heat exchanged is given by, Q = ΔU + W
Using equations (1) and (2) we get,
Q = nCV(Tf – Ti) + nR(Tf – Ti)
∴ Q = (nCV + nR) (Tf – Ti)
∴ Q = nCp(Tf – Ti) .............(∵ Cp = CV + R)
Where, Cp is the specific heat at constant pressure. - The p-V diagram for an isobaric process is called isobar. It is shown in the figure below.

APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Explain why The climate of a harbour town is more temperate than that of a town in a desert at the same latitude.
Answer in brief.
Why should a Carnot cycle have two isothermal two adiabatic processes?
An ideal gas is taken through an isothermal process. If it does 2000 J of work on its environment, how much heat is added to it?
An ideal gas of volume 2 L is adiabatically compressed to (1/10)th of its initial volume. Its initial pressure is 1.01 x 105 Pa, calculate the final pressure. (Given 𝛾 = 1.4)
Explain graphically (i) positive work with varying pressure, (ii) negative work with varying pressure, and (iii) positive work at constant pressure.
Explain thermodynamics of the adiabatic process.
When you exercise in the morning, by considering your body as a thermodynamic system, which of the following is true?
The V-T diagram of an ideal gas which goes through a reversible cycle A→B→C→D is shown below. (Processes D→A and B→C are adiabatic)
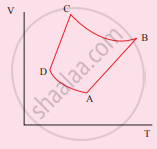
The corresponding PV diagram for the process is (all figures are schematic)
Give the equation of state for an isothermal process.
Apply first law for an isothermal process.
Draw the PV diagram for the isobaric process.
What is a cyclic process?
What is meant by a reversible and irreversible processes?
In an adiabatic expansion of the air, the volume is increased by 4%, what is the percentage change in pressure? (For air γ = 1.4)
A monoatomic gas of pressure p having volume V expands isothermally to a volume 2V and then adiabatically to a volume 16V. The final pressure of the gas is ____________.
`("ratio of specific heats" = 5/3)`
For an isothermal expansion of a perfect gas, the value of `(Delta "P")/"P"` is equal to ____________.
In an isothermal process, the volume of an ideal gas is halved. One can say that ____________.
Ideal gas for which 'ϒ' = 1.5 is suddenly compressed to `1/4`th of its initial volume. The ratio of 4 the final pressure to the initial pressure is ______.
`(ϒ = "C"_"p"/"C"_"v")`
The work done on the system in changing the state of a gas adiabatically from equilibrium state A to equilibrium state B is 22.4 J. If the gas is taken from state A to B through another process in which the net heat absorbed by the system is 15.5 cal, then the net work done by the system in the latter case is ______.
( l cal = 4.2 J)
Consider P-V diagram for an ideal gas shown in figure.
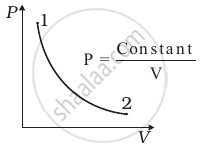
Out of the following diagrams (figure), which represents the T-P diagram?
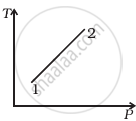 (i) |
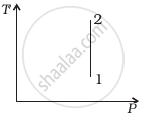 (ii) |
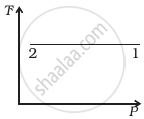 (iii) |
 (iv) |
Give any two types of a thermodynamic process.
When an inflated ballon is suddenly burst, why is the emerging air slightly cooled?
An ideal gas is taken through a cyclic process ABCDA as shown in figure. The net work done by the gas during the cycle is ______.
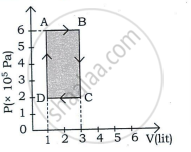
Explain how can a gas be expanded at constant temperature.
