Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Differentiate between the reversible and irreversible processes.
उत्तर
| Sr. No. | Reversible process | Irreversible process |
| i. | A reversible process is a change that can be retraced in a reverse (opposite) direction. | An irreversible process is a change that cannot be retraced in a reverse (opposite) direction. |
| ii. | The path of a reversible process is the same in the forward and the reverse direction. | The path of an irreversible process is not the same in the forward and the reverse direction. |
| iii. | Reversible changes are very slow and there is no loss of any energy in the process. | There is a permanent loss of energy from the system due to friction or other dissipative forces in an irreversible process. |
| iv. | The system comes back to its initial state after it is taken along the reverse path. | The change of state depends upon the path taken to change the state during an irreversible process. |
| v. | Reversible processes are ideal processes. | Irreversible processes are real processes. |
| vi. |
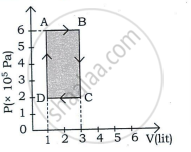
p-V diagram:
|
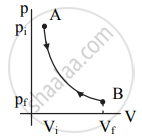
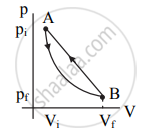
p-V diagram:
|
संबंधित प्रश्न
A thermodynamic system is taken from an original state to an intermediate state by the linear process shown in Figure

Its volume is then reduced to the original value from E to F by an isobaric process. Calculate the total work done by the gas from D to E to F
Heating a gas in a constant volume container is an example of which process?
What is a thermodynamic process?
Explain the cyclic process.
Write a note on free expansion.
Explain work done during a thermodynamic process.
When a cycle tyre suddenly bursts, the air inside the tyre expands. This process is ____________.
When food is cooked in a vessel by keeping the lid closed, after some time the steam pushes the lid outward. By considering the steam as a thermodynamic system, then in the cooking process
When you exercise in the morning, by considering your body as a thermodynamic system, which of the following is true?
Give an expression for work done in an isothermal process.
Apply first law for an isothermal process.
Apply first law for an isobaric process.
Draw the PV diagram for the isochoric process.
What is meant by a reversible and irreversible processes?
Can the given heat energy be completely converted to work in a cyclic process? If not, when can the heat can completely converted to work?
Explain in detail the isothermal process.
Derive the work done in an isothermal process.
An ideal gas is made to go from a state A to stale B in the given two different ways (see figure) (i) an isobaric and then an isochoric process and (ii) an isochoric and then an isobaric process. The work done by gas in the two processes are W1 and W2 respectively. Then,

One mole of an ideal gas with `gamma` = 1.4 is adiabatically compressed so that its temperature rises from 27° C to 47° C. The change in the internal energy of the gas is (R = 8.3 J/mol.K) ____________.
Two identical samples of a gas are allowed to expand (i) isothermally (ii) adiabatically. Work done is ____________.
In which of the following processes, beat is neither absorbed nor released by a system?
For an isothermal expansion of a perfect gas, the value of `(Delta "P")/"P"` is equal to ____________.
In an isothermal process, the volume of an ideal gas is halved. One can say that ____________.
An ideal gas is compressed to half its initial volume by means of several processes. Which of the process results in the maximum work done on the gas?
We consider a thermodynamic system. If `Delta"U"` represents the increase in its internal energy and W the work done by the system, which of the following statements is true?
Give any two types of a thermodynamic process.
In a certain thermodynamical process, the pressure of a gas depends on its volume as kV3. The work done when the temperature changes from 100°C to 300°C will be ______ nR, where n denotes number of moles of a gas.
An ideal gas is taken through a cyclic process ABCDA as shown in figure. The net work done by the gas during the cycle is ______.