Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Explain the histological structure of testis.
Describe histological structure of Testis with well labelled diagram.
With the help of a suitable diagram describe histology of testis.
उत्तर
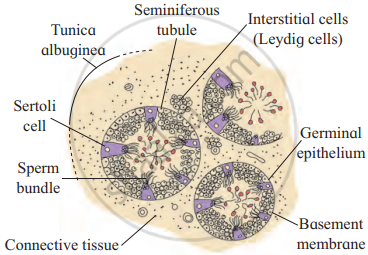
T. S. of Testis
Histology of Testis:
- Externally, the testis is covered by three layers. These are:
- Tunica vaginalis: It is the outermost incomplete peritoneal covering made up of connective tissue and epithelium.
- Tunica albuginea: It is the middle layer formed by collagenous connective tissue.
- Tunica vasculosa/vascularis: It is the innermost layer. It is a thin and membranous layer.
- Each testis is divided into about 200-300 testicular lobules by fibres from Tunica albuginea. Each lobule has 1 to 4 highly coiled seminiferous tubules.
- Each seminiferous tubule is internally lined by a single layer of cuboidal germinal epithelial cells (spermatogonia) and a few large pyramidal cells called Sertoli or sustentacular cells.
- The germinal epithelial cells undergo gametogenesis to form spermatozoa.
- Sertoli cells provide nutrition to the developing sperm.
- Various stages of spermatogenesis can be seen in the seminiferous tubules. The innermost spermatogonial cell (2n), primary spermatocyte (2n), secondary spermatocyte (n), spermatids, (n) and sperms (n).
- Between seminiferous tubules, few groups of interstitial cells (Cells of Leydig) are present
- After puberty, interstitial cells produce a type of androgen, i.e., testosterone.
संबंधित प्रश्न
What is the effect of DNA copying, which is not perfectly accurate, on the reproduction process? How does the amount of DNA remain constant though each new generation is a combination of DNA copies of two individuals?
How do organisms, whether reproduced asexually or sexually maintain a constant chromosome number through several generations? Explain with the help of suitable example.
Define sexual reproduction.
One of the following process does not lead to the formation of clones. This is :
(a) fission
(b) fertilisation
(c) fragmentation
(d) tissue culture
Answer in one sentence.
Enlist the external genital organs in the female.
Write an account of the seminal vesicle and bulbourethral gland in the male reproductive system.
Animals which give birth to young ones directly are named as ______.
The zygote divides repeatedly into a group of cells, which develops into different tissues and organs constituting a full body. This structure is known as ______.
Explain how stability of the DNA of the species is ensured in sexually reproducing organisms.
