Advertisements
Advertisements
Questions
Explain the histological structure of testis.
Describe histological structure of Testis with well labelled diagram.
With the help of a suitable diagram describe histology of testis.
Solution
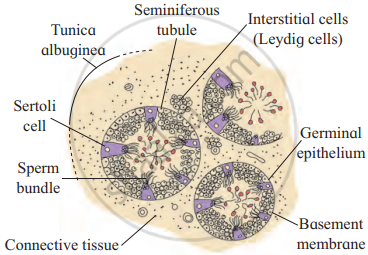
T. S. of Testis
Histology of Testis:
- Externally, the testis is covered by three layers. These are:
- Tunica vaginalis: It is the outermost incomplete peritoneal covering made up of connective tissue and epithelium.
- Tunica albuginea: It is the middle layer formed by collagenous connective tissue.
- Tunica vasculosa/vascularis: It is the innermost layer. It is a thin and membranous layer.
- Each testis is divided into about 200-300 testicular lobules by fibres from Tunica albuginea. Each lobule has 1 to 4 highly coiled seminiferous tubules.
- Each seminiferous tubule is internally lined by a single layer of cuboidal germinal epithelial cells (spermatogonia) and a few large pyramidal cells called Sertoli or sustentacular cells.
- The germinal epithelial cells undergo gametogenesis to form spermatozoa.
- Sertoli cells provide nutrition to the developing sperm.
- Various stages of spermatogenesis can be seen in the seminiferous tubules. The innermost spermatogonial cell (2n), primary spermatocyte (2n), secondary spermatocyte (n), spermatids, (n) and sperms (n).
- Between seminiferous tubules, few groups of interstitial cells (Cells of Leydig) are present
- After puberty, interstitial cells produce a type of androgen, i.e., testosterone.
RELATED QUESTIONS
Name two main processes of sexual reproduction
What are chromosomes?
How do organisms, whether reproduced asexually or sexually maintain a constant chromosome number through several generations? Explain with the help of suitable example.
How does reproduction help in providing stability to populations of species?
Define Juvenile phase,
Mention the common method of reproduction in Start fish.
Meiosis is an essential event in the sexual life cycle of any organism. Give two reasons.
Answer the following question.
Which is the function of male accessory glands?
Zygote develop a thick wall that is resistant to dessication and damage is present in ______.
