Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Explain the process of transcription in prokaryotes.
उत्तर
Transcription is the process of the formation of the m-RNA strand on a DNA strand in the nucleus. It takes place in three steps—initiation, elongation and termination.
(a) Initiation:
i. In prokaryotes, the structural genes are polycistronic and continuous.
ii. A single DNA-dependent RNA polymerase catalyses transcription of all the three types of RNA (mRNA, tRNA and rRNA).
iii. RNA polymerase binds to the promoter region and starts the process of transcription. The RNA polymerase enzyme contains a detachable subunit called the sigma (σ) factor. It helps the enzyme to bind firmly to DNA.
iv. The RNA core polymerase (minus sigma factor) moves down DNA at a faster pace and this continues to synthesise a new RNA chain.
(b) Elongation:
i. Ribonucleoside triphosphates help in the polymerisation on a DNA template, following the rule of complementarity.
ii. The enzyme facilitates the opening of the DNA helix and continues elongation.
(c) Termination: The process of elongation during transcription continues until the enzyme, RNA core polymerase reaches the terminator sequence in the sense DNA strand (3′–AAAAAAT–5′). At this point, another protein particle, the rho (ρ) factor, forms a complex with RNA-polymerase. This causes the enzyme to go off the DNA track, and thus, new m-RNA is released.

APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Following are the features of genetic codes. What does each one indicate?
Stop codon; Unambiguous codon; Degenerate codon; Universal codon.
Initiation codon of protein synthesis in Eukaryotes is ______.
What is the central dogma?
What is the central dogma?
A mRNA molecule is produced by ____________.
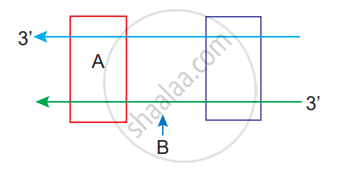
Name the parts marked ‘A’ and ‘B’ in the given transcription unit:
DNA template sequence of CTGATAGC is transcribed over mRNA as ______.
Which is not involved in protein synthesis?
In a cell, DNA transcription is halted when ______
Read the following and answer from given below:
The translation is the process of polymerization of amino acids to form a polypeptide. The order and sequence of amino acids are defined by the sequence bases in the mRNA. The amino acids are joined by a bond called a peptide bond. The ribosome is the site of protein synthesis.
Which ion is essential for the association of both units of the ribosome at the time of protein formation?
