Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Explain the various steps involved in the process of control.
Explain the following as steps in the process of controlling:
- Setting performance Standards
- Measurement of actual performance
State the steps in the process of controlling.
Describe briefly the steps in the process of controlling.
Explain the various steps in the process of controlling.
Explain the steps in the controlling process.
Explain the Process of Controlling.
Explain the first two steps in the process of controlling.
'Analysing deviations' is an important step in the process of controlling. It is therefore important to focus on key result areas which are critical to the success of an organization. Identify and give the meaning of the concept discussed above.
Explain the following as steps in the process of controlling:
- Analysing Deviations, and
- Taking Corrective Action
Explain -
- Critical point control
- Management by exception with respect to Analyzing deviations, a step in the process of controlling. Give a suitable example.
Explain Critical point control and Management by exception, as an important part of 'Atlalysing Deviations' a step in the process of controlling.
Explain the various steps involved in the process of controlling, as a function of Management.
उत्तर
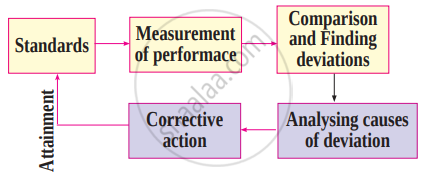
Controlling is a systematic approach of managing and controlling the organisational actions. The following are the steps involved in the controlling process.
- Setting Standards - Setting up of standards involves developing the benchmarks against which the actual performance is to be measured. The standards can be set in qualitative as well as quantitative terms. Qualitative benchmarks can be in the form of improving coordination in work, higher goodwill or increased motivation level of employees, etc. For example, to improve the motivation level among employees, standard can be set in terms of number of initiatives taken. Quantitative benchmarks can be in the form of sales targets, units to be produced or time to be spent on a particular action, etc. For example, in a shirt factory completing 10 pieces a day is a quantitative target. The standards that are set should be such that they facilitate easy comparison.
- Measuring Actual Performance - Once the standards are set, the next step is to measure the actual performance of the activities. This may be done through various techniques such as personal observation, checking the sample, performance reports, etc. The checking should be done in an exact and reliable manner so that correct measurement is taken for comparison. Measurement can be done after the completion of an activity as well as while it is in progress. For example, while assembling small parts of a bigger machine, the parts can be checked before assembling. This would ensure the continuous monitoring of the small parts as well as the final machine.
- Comparing the Performances - Performances once measured are then compared with the set standards. Such a comparison helps in assessing the deviations in the work. Thereby, it guides the managers in taking the necessary steps to improve the performances. These comparisons are easier when they are in quantitative terms. For example, efficiency in work in terms of cost incurred can be measured against the standard cost.
- Analysing Deviation - Every organisation faces deviations when comparing the actual performance with the pre-developed standards. Thus, it is important to find the deviations that are in the permissible range. It is said that deviations in key areas should be attended first. For analysing the deviations the managers generally use 'Critical Point Control' and 'Management by Exception'. .
- Critical Point Control: An organisation cannot keep a check on all the activities of the management. Thus, this technique of controlling aims at focussing on only the key result areas (KRAs) that affect the entire organisation. For example, rise in input cost would be more important than rise in stationary cost.
- Management by Exception: This technique of management is based on the belief that 'an attempt to control everything results in controlling nothing'. According to this, only the essential and significant deviations that are beyond the acceptable limit should be controlled. For example, if there is a 6 per cent rise in labour cost whereas the permissible limit is just 3 per cent, then, this should be immediately brought into the notice of the management. On the other hand a 2 percent rise in the cost can be ignored. Once the deviations are recognised, it is necessary to acknowledge the cause for them. There can be a number of elements causing deviations in work such as infeasible standards, deficiencies in process, under utilisation of resources, changes in business environment, etc. Thus, it becomes important for the management to take into regard the causes of the concerned deviations.
- Corrective Measures - When deviations go beyond the admissible limits, there arises a need for the management to take corrective actions. This is the last step of controlling which aims at correcting the deficiencies of the organisation so that the errors do not occur again. For example, if the production target was not met duly, appropriate corrective actions such as training the workers or updating the machinery for working, etc. can be taken.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
State the steps in the controlling process.
State any one situation in which an organisation’s control system loses is effectiveness
______ refers to the function of evaluating and assessing the progress of the work done
Which of the following steps in controlling process involves developing of the benchmarks against which the actual performance is to be measured?
Which of the following steps in controlling process involves " to measure the actual performance of the activities"
Which of the following points highlight the problems faced by the organisation when implementing an effective controlling system?
What should be the 'focus point' for a manager while controlling, as controlling at each and every step is not possible?
Assertion (A): The controlling function measures progress towards the organisational goals.
Reason (R): Controlling guides the organisation and keeps it on the right track so that organisational goals might be achieved.
Assertion (A): Controlling creates an atmosphere of order and discipline in the organisation.
Reason (R): Controlling helps to minimise dishonest behaviour on the part of the employees by keeping a close check on their activities.
Which of the following steps in the Controlling process state that comparison becomes easier when standards are set in quantitative terms?
What should be the 'focus point' for a manager while controlling, as controlling at each and every step is not possible?
Corrective action is a part of:
What should be the 'focus point' for a manager while controlling, as controlling at each and every step is not possible?
Controlling is a/an ______ process as it ensures completion of organisational goals by monitoring the actual performance.
Read the following text and answer the following question on the basis of the same:
A critical point control (CPC) approach is followed by McDonald in the cooking and handling process so that any food safety threat can be prevented, eliminated, or reduced to an acceptable level. Hence, continuous monitoring of activities are undertaken to ensure that the process is right at each critical point control. The main principle followed for cooking at McDonald is "less amount many time" which can ensure the high quality and high fresh level of the food. For instance, if four hamburgers have to be made, a worker cannot cook all the four hamburgers at one time. The time figured out for making hamburger is one hundred and forty-five seconds. moreover, nearly all foods in the McDonald have the specific holding time for hamburgers is ten minutes and for french fries is seven minutes. If it is not sold within that time it is thrown away. Also, the temperature of the milk sent by the supplier must be under 4°C, otherwise it will be returned.
Which of the following steps involved in the controlling process is discussed in the above lines?
Read the following text and answer the following question on the basis of the same:
A critical point control (CPC) approach is followed by McDonald in the cooking and handling process so that any food safety threat can be prevented, eliminated, or reduced to an acceptable level. Hence, continuous monitoring of activities are undertaken to ensure that the process is right at each critical point control. The main principle followed for cooking at McDonald is "less amount many time" which can ensure the high quality and high fresh level of the food. For instance, if four hamburgers have to be made, a worker cannot cook all the four hamburgers at one time. The time figured out for making hamburger is one hundred and forty-five seconds. moreover, nearly all foods in the McDonald have the specific holding time for hamburgers is ten minutes and for french fries is seven minutes. If it is not sold within that time it is thrown away. Also, the temperature of the milk sent by the supplier must be under 4°C, otherwise it will be returned.
Identify the point which highlights the importance of the controlling function in the above text.
Some employees have been assigned the job of measuring the output in an objective and reliable way. They are applying different techniques for achieving this aim. Some of these are personal-observation, sample-checking etc. They are also keeping the units of measurement same as that of the units in the standards.
Name the step of ‘Controlling process applicable in the above paragraph.
Enumerate any three advantages of Management by Exception which is used by manager in analysing deviations.
Explain process of controlling.
Controlling is a systematic process involving a series of steps. Explain these steps of Controlling.
