Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Explain why the planets do not twinkle.
Explain why, the planets do not twinkle at night.
उत्तर
Planets are much closer to the Earth and are seen as extended sources. So, a planet may be considered a collection of a large number of point-sized light sources. Although light coming from individual point-sized sources flickers but the total amount of light entering our eye from all the individual point-sized sources averages out to be constant. Thereby, planets appear equally bright and there is no twinkling of planets.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
What is atmospheric refraction? Use this phenomenon to explain the following natural events:
Advanced sun-rise and delayed sun-set.
Draw diagrams to illustrate your answers.
The correct sequencing of angle of incidence, angle of emergence, angle of refraction and lateral displacement shown in the following diagram by digits 1, 2, 3 and 4 is:
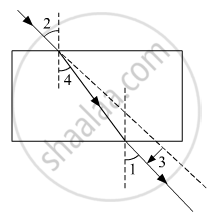
(a) 2, 4, 1, 3
(b) 2, 1, 4, 3
(c) 1, 2, 4, 3
(d) 2, 1, 3, 4
The phenomenon that causes the twinkling of stars is refraction of light.
Name two effects produced by the atmospheric refraction.
Atmospheric refraction causes advance sunrise and delayed sunset. By how much time is:
sunset delayed?
State whether the following statement is true or false:
The planets twinkle at night due to atmospheric refraction of light.
What is atmospheric refraction? What causes atmospheric refraction?
The atmospheric refraction of light causes the twinkling of:
(a) planets only
(b) stars only
(c) planets and stars
(d) stars and satellites
The stars appear higher in the sky than they actually are, due to:
(a) diffraction of light
(b) scattering of light
(c) refraction of light
(d) reflection of light
Due to atmospheric refraction of sunlight, the time from sunrise to sunset is lengthened by about:
(a) 6 minutes
(b) 2 minutes
(c) 4 minutes
(d) 5 minutes
The day is longer on the earth by about 4 minutes because:
(a) the earth is round in shape
(b) the earth rotates on its axis
(c) the earth revolves around the sun
(d) the earth has atmosphere
A student claims that because of atmospheric refraction, the sun can be seen after it has set, and the day is, therefore, longer than if the earth had no atmosphere.
What does the student mean by saying that the sun can be seen after it has set?
A student claims that because of atmospheric refraction, the sun can be seen after it has set, and the day is, therefore, longer than if the earth had no atmosphere.
Do you think that the students conclusion is correct?
What causes the scattering of blue component of sunlight in the atmosphere?
The stars appear higher from horizon than they actually are. Explain why it is so.
Explain why the planets do not twinkle but the stars twinkle.
Explain the refraction of light through a triangular glass prism using a labelled ray diagram. Hence define the angle of deviation.
How does refraction take place in the atmosphere? Why do stars twinkle but not the planets?
