Advertisements
Advertisements
Questions
Explain why the planets do not twinkle.
Explain why, the planets do not twinkle at night.
Solution
Planets are much closer to the Earth and are seen as extended sources. So, a planet may be considered a collection of a large number of point-sized light sources. Although light coming from individual point-sized sources flickers but the total amount of light entering our eye from all the individual point-sized sources averages out to be constant. Thereby, planets appear equally bright and there is no twinkling of planets.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
What is atmospheric refraction? Use this phenomenon to explain the following natural events:
Advanced sun-rise and delayed sun-set.
Draw diagrams to illustrate your answers.
The correct sequencing of angle of incidence, angle of emergence, angle of refraction and lateral displacement shown in the following diagram by digits 1, 2, 3 and 4 is:
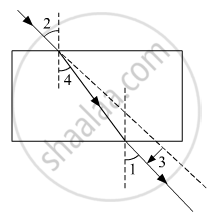
(a) 2, 4, 1, 3
(b) 2, 1, 4, 3
(c) 1, 2, 4, 3
(d) 2, 1, 3, 4
The phenomenon that causes the twinkling of stars is refraction of light.
Name two effects produced by the atmospheric refraction.
Atmospheric refraction causes advance sunrise and delayed sunset. By how much time is:
sunset delayed?
Why do stars seem higher than they actually are? Illustrate your answer with the help of a diagram.
The twinkling of stars is due to atmospheric:
(a) reflection of light
(b) dispersion of light
(c) interference of light
(d) refraction of light
As light from a far off star comes down towards the earth:
(a) it bends away from the normal
(b) it bends towards the normal
(c) it does not bend at all
(d) it is reflected back
Due to atmospheric refraction of sunlight, the time from sunrise to sunset is lengthened by about:
(a) 6 minutes
(b) 2 minutes
(c) 4 minutes
(d) 5 minutes
We know that light refracts (or bends) when it goes from one medium to another. Now, the atmosphere contains only air. Then how does light get refracted on passing through only air in the atmosphere?
By how much time the day would have been shorter if the earth had no atmosphere?
Why does the sky appear blue on a clear day?
What causes the scattering of blue component of sunlight in the atmosphere?
The stars appear higher from horizon than they actually are. Explain why it is so.
Refraction of light by the earth’s atmosphere due to variation in air density is called ____________.
Explain the refraction of light through a triangular glass prism using a labelled ray diagram. Hence define the angle of deviation.
How does refraction take place in the atmosphere? Why do stars twinkle but not the planets?
