Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
For the given cell, \[\ce{Mg | Mg^{2+} || Cu^{2+} | Cu}\]
(i) \[\ce{Mg}\] is cathode
(ii) \[\ce{Cu}\] is cathode
(iii) The cell reaction is \[\ce{Mg^+ Cu^{2+} -> Mg^{2+} + Cu}\]
(iv) \[\ce{Cu}\] is the oxidising agent
उत्तर
(ii) \[\ce{Cu}\] is cathode
(iii) The cell reaction is \[\ce{Mg^+ Cu^{2+} -> Mg^{2+} + Cu}\]
Explanation:
(i) Left side of cell reaction represents oxidation half-cell i.e., oxidation of \[\ce{Mg}\] and right side of cell represents reduction half-cell reactions i.e., reduction of copper.
(ii) \[\ce{Cu}\] is reduced and reduction occurs at cathode.
(iii) \[\ce{Mg}\] is oxidized and oxidation occurs at anode.
(iv) Whole cell reaction can be written as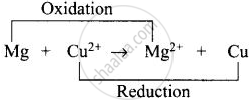
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Why cannot we store AgNO3 solution in copper vessel?
E°cell for the given redox reaction is 2.71 V
Mg(s) + Cu2+ (0.01 M) → Mg2+ (0.001 M) + Cu(s)
Calculate Ecell for the reaction. Write the direction of flow of current when an external opposite potential applied is
(i) less than 2.71 V and
(ii) greater than 2.71 V
How many moles of electrons are required for reduction of 2 moles of Zn2+ to Zn?
A gas X at 1 atm is bubbled through a solution containing a mixture of 1MY− and 1MZ− at 25°C. If the reduction potential of Z > Y > X, then ____________.
For the cell \[\ce{Mg_{(s)}|Mg^{2+}_{( aq)}||Ag^+_{( aq)}|Ag_{(s)}}\], calculate the equilibrium constant at 25°C and maximum work that can be obtained during operation of cell.
Given: \[\ce{E^0_{{Mg^{2+}|Mg}}}\] = −2.37 V and \[\ce{E^0_{{Ag^{+}|Ag}}}\] = 0.80 V
`E_(cell)^Θ` for some half cell reactions are given below. On the basis of these mark the correct answer.
(a) \[\ce{H^{+} (aq) + e^{-} -> 1/2 H_2 (g); E^Θ_{cell} = 0.00V}\]
(b) \[\ce{2H2O (1) -> O2 (g) + 4H^{+} (aq) + 4e^{-}; E^Θ_{cell} = 1.23V}\]
(c) \[\ce{2SO^{2-}_{4} (aq) -> S2O^{2-}_{8} (aq) + 2e^{-}; E^Θ_{cell} = 1.96V}\]
(i) In dilute sulphuric acid solution, hydrogen will be reduced at cathode.
(ii) In concentrated sulphuric acid solution, water will be oxidised at anode.
(iii) In dilute sulphuric acid solution, water will be oxidised at anode.
(iv) In dilute sulphuric acid solution, \[\ce{SO4^{2-}}\] ion will be oxidised to tetrathionate ion at anode.
What is electrode potential?
Consider the following diagram in which an electrochemical cell is coupled to an electrolytic cell. What will be the polarity of electrodes ‘A’ and ‘B’ in the electrolytic cell?
What should be the signs (positive/negative) for \[\ce{E^0_{cell}}\] and ΔG0 for a spontaneous redox reaction occurring under standard conditions?
What is an electrochemical cell? What does it consist of?
