Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Molar conductivity of ionic solution depends on:
(i) temperature.
(ii) distance between electrodes.
(iii) concentration of electrolytes in solution.
(iv) surface area of electrodes.
उत्तर
(i) temperature.
(iii) concentration of electrolytes in solution.
Explanation:
\[\ce{Λ_m (Scm^2mol^{-1}) = K}\]
On increasing the temperature molar conductivity increases whereas molar conductivity decreases on increasing the concentration.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
State Kohlrausch Law
Calculate the degree of dissociation (α) of acetic acid if its molar conductivity (Λm) is 39.05 S cm2 mol−1.
Given λ°(H+) = 349.6 S cm2 mol−1 and λ°(CH3COO−) = 40.9 S cm2 mol−1
In the plot of molar conductivity (∧m) vs square root of concentration (c1/2), following curves are obtained for two electrolytes A and B:
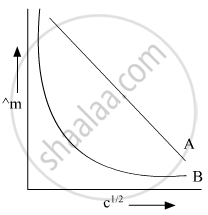
Answer the following:
(i) Predict the nature of electrolytes A and B.
(ii) What happens on extrapolation of ∧m to concentration approaching zero for electrolytes A and B?
Molar conductivity denoted by the symbol Λm is related to the conductivity of the solution by the equation (k is the conductivity and c is the concentration).
Solutions of two electrolytes ‘A’ and ‘B’ are diluted. The Λm of ‘B’ increases 1.5 times while that of A increases 25 times. Which of the two is a strong electrolyte? Justify your answer. Graphically show the behavior of ‘A’ and ‘B’.
The molar conductance of \[\ce{NaCl, HCl}\] and \[\ce{CH3COONa}\] at infinite dilution are 126.45, 426.16 and 91.0 S cm2 mol−1 respectively. The molar conductance of \[\ce{CH3COOH}\] at infinite dilution is. Choose the right option for your answer.
Molar conductivity of substance “A” is 5.9 × 103 S/m and “B” is 1 × 10–16 S/m. Which of the two is most likely to be copper metal and why?
The solubility of Co2[Fe(CN)6] in water at 25°C from the following data:
Conductivity of saturated solution of Co2[Fe(CN)6] = 2.06 × 10−6 ohm−1 cm−1 and that of water = 4.1 × 10−7 ohm−1 cm−1. The ionic molar conductivities of Co2+ and [Fe(CN)6]4− are 86 and 444 ohm−1 cm2 mol−1 respectively, is ______ × 10−6 mol/L.
Assertion (A) : Conductivity decreases with decrease in concentration of electrolyte.
Reason (R) : Number of ions per unit volume that carry the current in a solution decreases on dilution.
Conductivity of 2 × 10−3 M methanoic acid is 8 × 10−5 S cm−1. Calculate its molar conductivity and degree of dissociation if `∧_"m"^0` for methanoic acid, is 404 S cm2 mol−3.
