Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Give an example of motion in which speed remains uniform, but the velocity changes.
उत्तर
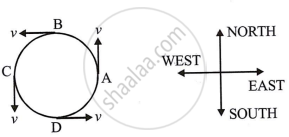
Direction of velocity in uniform circular motion
A particle travelling anticlockwise in a circular path with a constant speed v in a horizontal plane. The particle travels in the same amount of time (t = T/4) across each quarter of circles AB, BC, CD, and DA, where T is the particle's round-trip time on the circular path. Particle speed is therefore constant. However, at various places throughout the circular course, the particle's force direction of motion varies.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Read the statement below carefully and state, with reason, if it is true or false:
The acceleration vector of a particle in uniform circular motion averaged over one cycle is a null vector.
Is it possible to have an accelerated motion with a constant speed? Explain
Why is the motion of a body moving with a constant speed around a circular path said to be accelerated?
A particle performs uniform circular motion in a horizontal plane. The radius of the circle is 8 cm. The centripetal force acting on the particle is 15 N. Its kinetic energy is ____________.
A particle is perfonning uniform circular motion. If 'θ', 'ω', 'α' and ' a' are its angular displacement, angular velocity, angular acceleration, and centripetal acceleration respectively, then which of the following is 'WRONG'?
The given graph represents motion with ______ speed.
A body moving along a circular path of radius R with velocity v, has centripetal acceleration a. If its velocity is made equal to 2v. What will be the centripetal acceleration?
Earth also moves in circular orbit around sun once every year with on orbital radius of 1.5 × 1011 m. What is the acceleration of earth (or any object on the surface of the earth) towards the centre of the sun? How does this acceleration compare with g = 9.8 m/s2?
A wheel rotating at the same angular speed undergoes constant angular retardation. After the revolution, angular velocity reduces to half its initial value. It will make ______ revolution before stopping.
A particle moves along a circle of radius r with constant tangential acceleration. If the velocity of the particle is v at the end of second revolution, after the revolution has started, then the tangential acceleration is ______.
