Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Give the construction and working of photo emissive cell.
उत्तर
Photo emissive cell: Its working depends on the electron emission from a metal cathode due to irradiation of light or other radiations.
Construction:
1. It consists of an evacuated glass or quartz bulb in which two metallic electrodes – that is, a cathode and an anode are fixed.
2. The cathode C is semi-cylindrical in shape and is coated with a photo sensitive material. The anode A is a thin rod or wire kept along the axis of the semi-cylindrical cathode.
3. A potential difference is applied between the anode and the cathode through a galvanometer G.
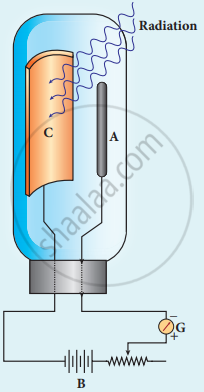
Construction of photo cell
Working:
When the cathode is irradiated with suitable radiation, electrons are emitted from it. These electrons are attracted by the anode and hence a current is produced which is measured by the galvanometer.
For a given cathode, the magnitude of the current depends on
- the intensity to incident radiation and
- the potential difference between anode and cathode.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A photoelectric surface is illuminated successively by monochromatic light of wavelength λ and `λ/2`. If the maximum kinetic energy of the emitted photoelectrons in the second case is 3 times that in the first case, the work function of the material is
If the mean wavelength of light from sun is taken as 550 nm and its mean power as 3.8 × 1026 W, then the average number of photons received by the human eye per second from sunlight is of the order of
Give the definition of intensity of light according to quantum concept and its unit.
Define stopping potential.
What is a surface barrier?
Explain the effect of potential difference on photoelectric current.
Obtain Einstein’s photoelectric equation with the necessary explanation.
List out the characteristics of photons.
A 3310 Å photon liberates an electron from a material with energy 3 × 10−19 J while another 5000 Å photon ejects an electron with energy 0.972 × 10−19 J from the same material. Determine the value of Planck’s constant and the threshold wavelength of the material.
At the given point of time, the earth receives energy from the sun at 4 cal cm–2 min–1. Determine the number of photons received on the surface of the Earth per cm2 per minute. (Given: Mean wavelength of sunlight = 5500 Å)
