Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Growth hormone is important for normal growth. Justify the statement.
उत्तर
Growth hormone promotes growth of all the tissues and the metabolic process of the body. It influences the metabolism of carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids. It increases the rate of protein biosynthesis in the cells.
It stimulates chondrogenesis (cartilage formation), osteogenesis (bone formation) and helps in the retention of minerals like nitrogen, potassium, phosphorus, sodium, etc in the body. It increases the release of fatty acid from adipose tissue and decreases the rate of glucose utilization for energy by the cells. The hyposecretion of growth hormones causes dwarfism in children.
संबंधित प्रश्न
Give an example of a blood pressure lowering hormone.
Describe the T. S. of thyroid gland
Define the following:
Endocrine glands
What would a child suffer from if there was hyposecretion from his thyroid?
Match the items of column I with those of column II
| Column I | Column II | ||
| 1 | β (beta) cells of islets of Langerhans |
a | condition due to undersecretion of thyroxine in adults |
| 2 | Thyroid | b | Glucocorticoids |
| 3 | Cretinism | c | Exophthalmic goitre |
| 4 | Addison's disease | d | Increases heart beat |
| 5 | Hypothyroidism | e | Thyroxine |
| 6 | Myxoedema | f | Adrenal cortex |
| 7 | Adrenaline Under secretion of thyroxine in a child |
h | Under secretion of thyroxine in a child |
Mention which of the statements are true (T) and which are false (F). Give reason in support of your answer.
Harmones ‘obey’ the commands like ‘enough, slow down or ‘two little, speed up’
Mention any two differences between a hormone and an enzyme.
Compare the hormonal response with the nervous response with respect to their speed, transmission and the general nature of changes brought about.
Identify the ODD term in each set and name the CATEGORY to which the remaining three belong :
Example : glucose, starch, cellulose, calcium
Odd term : calcium
Category : others are different types of carbohydrates
Addison’s disease, Cushing’s Syndrome, Acromegaly, Leukemia
The diagram give below represents an endocrine gland in the human body. Study the diagram and answer the following questions: 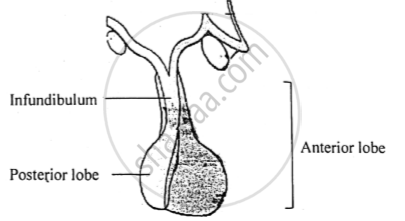
Explain the term ‘Hormone’. What is the role of Tropic hormones in the human body?
Name the hormone responsible for the following function:
Ossification of bones
Choose the correct answer:
Which one of the following is not an endrocine gland?
Choose the correct answer:
An organ, tissue or cell where a hormone produces its effects is known as __________
Complete the following:
| Gland/Organ | Hormone | Function |
| (i) Stomach | __________ | __________ |
| (ii) Parathyroid | __________ | __________ |
| (iii) __________ | __________ | Lowers blood sugar level. |
| (iv) Adrenal medulla | __________ | __________ |
| (v) Pancreas (Alpha cells) | __________ | __________ |
| (vi) Testes | __________ | __________ |
Complete the table given below by filling in the blanks numbered 1 to 8.
| Gland | Hormone Secreted | Effect on Body |
| 1 | 2 | Regulates basal metabolism |
| Pancreas (β-cells) | 3 | 4 |
| 5 | 6 | Increases heart beat |
| 7 | Thyroid stimulating hormone | 8 |
Hormones are called ‘chemical messengers’.
Differentiate: Acromegaly and Myxedema.
Give the Technical Term: Name two hormones secreted by the alimentary canal.
Give the Technical Term: Name the structure which produces testosterone.
Fill in the Blanks:
______ is called father of endocrinology.
Some of the endocrine glands are shown by the guidelines.

(i) Name the glands 1 to 5.
(ii) Name any two endocrine glands which are not shown in the diagram.
(iii) Name one gland which is both exocrine and endocrine.
State the Function
Thyroxin
State the Function
Oestradiol
Choose the Odd One Out
Choose the Odd One Out
Choose the Odd One Out
Choose the Odd One Out
Column ‘II’ is a list of items related to ideas in Column ‘I’. Match the term in Column ‘II’ with a suitable idea given in Column ‘I’.
| Column A | Column B |
| (i) Pituitary | (a) produces male sex characteristics |
| (ii) Ovaries | (b) decreases blood sugar level |
| (iii) Thyroid | (c) increases heart and breathing rate raises blood pressure |
| (iv) Thymus | (d) produces female sex characteristics |
| (v) Adrenals | (e) is known as emergency hormone |
| (vi) Hypothalamus | (f) regulates the level of calcium and phosphorus |
| (vii) Pancreas | (g) increases the rate of metabolism |
| (viii) Testes | (h) maintains the level of calcium |
| (ix) Parathyroid | regulates the amount of water excreted in the urine. |
| (x) Cretinism | (j) simulates skeletal growth |
| (xi) Diabetes mellitus | (k) regulates the activities of other glands |
| (xii) Insulin shock | (l) stimulates the development of male and female sex organs |
| (xiii) Gigantism | (m) Shortage of glucose in the blood. |
| (xiv) Enlargement of breasts in adult males | (n) Over-secretion of growth hormone |
| (xv) Exophthalmic goiter | (o) Excess of glucose in the blood |
| (xvi) Acromegaly | (p) Over-secretion of thyroxin |
| (xvii) Addison’s disease | (q) Dwarfism and mental retardation |
| (xviii)Cretinism | (r) Over-secretion of cortical hormones |
| (xix) Dwarfism | (s) Under-secretion of the adrenal cortex |
| (xx) Adrenalin | (t) Under-secretion of thyroxin in children |
| (xxi) Vasopressin | (u) Over-secretion of growth hormones in adults |
Which organ acts a temporary endocrine gland in females?
Iodised salt is essential to prevent ______.
Hormones are known as chemical messenger. Justify.
Write the role of oestrogen in ovulation?
Enumerate the role of kidney as an endocrine gland.
Acromegaly is caused by ______.
