Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
How does Hardy-Weinberg’s expression (p2+2pq+q2=1) explain that genetic equilibrium is maintained in a population? List any four factors that can disturb the genetic equilibrium.
उत्तर
The allele frequencies in a population are stable and are constant from generation to generation in the absence of gene flow, genetic drift, mutation, recombination, and natural selection. If a population is in a state of Hardy Weinberg equilibrium, the frequencies of alleles and genotypes or sets of alleles in that population will remain the same over generations. Evolution is a change in the allele frequencies in a population over time. Hence population in Hardy Weinberg is not evolving.
Suppose we have a large population of beetles, (infinitely large) and appear in two colours’ dark grey (black) and light grey, and their colour is determined by the ‘A’ gene. ‘AA’ and ‘Aa’ beetles are dark greys and ‘aa’ beetles are light grey. In a population let’s say that the ‘A’ allele has a frequency (p) of 0.3 and the ‘a’ allele has a frequency (q ) of 0.7. Then p + q = 1.
If a population is in Hardy Weinberg equilibrium the genotype frequencycan be estimated by Hardy Weinberg equation.
(p + q)2 = p2+ 2pq + q2
p2 = frequency of AA
2pq = frequency of Aa
q2 = frequency of aa
p = 0.3, q = 0.7 then,
p2 = (0.3)2 = 0.09 = 9 %AA
2pq = 2(0.3) (0.7) = 0.42 = 42 % Aa
q2 = (0.7)2 0.49 = 49 % aa
Hence the beetle population appears to be in Hardy - Weinberg equilibrium. When the beetles in Hardy - Weinberg equilibrium reproduce the allele and genotype frequency in the next generation would be: Let’s assume that the frequency of ‘A’ and ‘a’ allele in the pool of gametes that make the next generation would be the same, then there would be no variation in the progeny. The genotype frequencies of the parent appear in the next generation. (i.e. 9% AA, 42% Aa and 49% aa).
If we assume that the beetles mate randomly (selection of male gamete and female gamete in the pool of gametes), the probability of getting the offspring genotype depends on the genotype of the combining parental gametes.
संबंधित प्रश्न
p2 + 2pq + q2 = 1. Explain this algebraic equation on the basis of Hardy Weinberg's principle.
State Hardy-Weinberg’s principle.
Differentiate between Directional natural selection and Disruptive natural selection.
According to the Hardy-Weinberg principle, the allele frequency of a population remains constant. How do you interpret the change of frequency of alleles in a population?
Multiple choice question.
In Hardy - Weinberg equation, the frequency of homozygous recessive individual is represented by:
Very short answer question.
State the Hardy – Weinberg equilibrium.
Explain how mutations, natural selection and genetic drift affect Hardy Weinberg equilibrium.
Hardy - Weinberg equilibrium is known to be affected by gene - flow, genetic drift, mutation, genetic recombination and
Disturbance of Hardy - Weinberg equilibrium results in
In a certain population, the frequency of three genotypes is as follows:
| Genotypes: | BB | Bb | bb |
| frequency: | 22% | 62% | 16% |
What is the likely frequency of B and b alleles?
State and explain any three factors affecting allele frequency in populations.
How is Hardy-Weinberg's expression “(p2 + 2pq + q2) = 1” derived?
The graphs below show three types of natural selection. The shaded areas marked with arrows show the individuals in the population who are not selected. The dotted vertical lines show the statistical means.
 |
 |
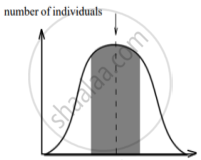 |
| character Graph A |
character Graph B |
character Graph C |
- What names are given to the types of selection shown in graphs A, B and C?
- After the selection has operated for several generations in the above populations indicated as, Graph A, B and C, graphically illustrate the probable results.
Explain Hardy-Weinberg's principle
State Hardy Weinberg's principle.
A population of 200 fruit flies is in Hardy Weinberg equilibrium. The frequency of the allele (a) 0.4. Calculate the following:
The number of homozygous recessive fruit flies.
A population of 200 fruit flies is in Hardy Weinberg equilibrium. The frequency of the allele (a) 0.4. Calculate the following:
The number of carrier fruit flies.
The black colour on the beak of finches dominates over the yellow colour. There are 210 individuals with the genotype DD, 245 individuals with the genotype Dd and 45 individuals with the genotype dd. Deduce the frequency of individuals with dominant, heterozygous, and recessive traits.
