Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
How is sodium metal extracted? Explain with the help of equation of the reaction involved.
उत्तर
Sodium is extracted by electrolytic reduction of molten sodium chloride. On passing electricity through molten sodium chloride, decomposition occurs and sodium metal and chlorine gas are formed.
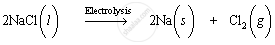
Molten sodium chloride contains sodium and chloride ions. The reactions that occur during electrolysis are:
1. The cathode produces electrons to reduce sodium ions to sodium atoms (or sodium metal) by acting as reducing agent. Sodium ions are cations; therefore, they are attracted to the negatively-charged cathode and get deposited there.
Cathode: 
Chloride ions are anions; therefore they are attracted to the positively-charged anode. These chloride ions are oxidised to chlorine gas. Chlorine gas is produced at the anode.
Anode: 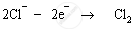
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A man went door to door posing as a goldsmith. He promised to bring back the glitter of old and dull gold ornaments. An unsuspecting lady gave a set of gold bangles to him which he dipped in a particular solution. The bangles sparkled like new but their weight was reduced drastically. The lady was upset, but after a futile argument, the man beat a hasty retreat. Can you play the detective to find out the nature of the solution he had used?
Explain why, carbon cannot reduce oxides of sodium or magnesium.
The metal which can be extracted from the bauxite ore is:
(a) Na
(b) Mn
(c) Al
(d) Hg
An important ore of zinc metal is:
(a) calamine
(b) cuprite
(c) pyrolusite
(d) haematite
Manganese metal is extracted from manganese dioxide by a reduction process by making use of:
(a) carbon
(b) hydrogen
(c) electrolysis
(d) aluminium
Define the following term.
Mineral
Arrange the metals of copper, iron, magnesium, sodium and zinc in the decreasing order of reactivity.
State three objectives achieved during the roasting of ores.
In the electrolytic method, a layer of highly active metal is applied to a less active metal.
Explain concept with example/explain with the help of a balanced equation.
Calcination
