Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
- State the relationship between mechanical advantage, velocity ratio and efficiency.
- Name the term that will not change for a machine of a given design.
उत्तर
Relation between M.A., V.R. and η
i. Efficiency = `"Work output"/"Work input"`
= `(L xx d_L)/(E xx d_E)`
= `(L/E)/((dE)/(dL))`
But `L/E` = M.A. and `(dE)/(dL)` = V.R.
Efficiency = η = `(M.A)/ (V.R.)` or M.A. = η × V.R.
ii. For a machine of a certain design, the term velocity ratio remains constant since M.A. = V.R.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Explain the term mechanical advantage.
Define the term velocity ratio.
When does a machine act as (a) a force multiplier, (b) a speed multiplier? Can a machine act as a force multiplier and a speed multiplier simultaneously?
How is the mechanical advantage related with the velocity ratio for an actual machine? State whether the efficiency of such a machine is equal to 1, less than 1 or more than 1.
Draw a diagram to illustrate the position of fulcrum load and effort, in the following:
A common balance
Draw a diagram to illustrate the position of fulcrum load and effort, in the following:
A nut cracker
Draw a diagram to illustrate the position of fulcrum load and effort, in the following:
Forceps
Figure below shows a wheel barrow of mass 15 kgf carrying a load of 30 kgf with its centre of gravity at A. The points B and C are the centre of wheel and tip of the handle such that the horizontal distance AB = 20 cm and AC = 40 cm.
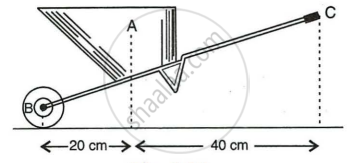
Find:
- the load arm,
- the effort arm,
- the mechanical advantage and
- the minimum effort required to keep the leg just off the ground.
A fire tongs has arms 20 cm long. It is used to lift a coal of weight 1.5 kgf by applying an effort at a distance 15 cm from the fulcrum. Find:
- the mechanical advantage of fire tongs and
- the effort needed.
Mechanical advantage = ______ × velocity ratio.
