Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
If the frequency of incident light falling on a photosensitive material is doubled, then the kinetic energy of the emitted photoelectron will be ______.
पर्याय
same as its initial value
two times its initial value
more than two times its initial value
less than two times its initial value
उत्तर
If the frequency of incident light falling on a photosensitive material is doubled, then the kinetic energy of the emitted photoelectron will be more than two times its initial value.
Explanation:
E = W0 + Kmax
⇒ Kmax = E − W0
= hv − W0
⇒ K1 = hv − W0 and
K2 = 2hv − W0
⇒ K2 > 2K1
संबंधित प्रश्न
Choose the correct option.
Polychromatic (containing many different frequencies) radiation is used in an experiment on the photoelectric effect. The stopping potential ______.
The threshold wavelength of tungsten is 2.76 x 10-5 cm.
(a) Explain why no photoelectrons are emitted when the wavelength is more than 2.76 x 10-5 cm.
(b) What will be the maximum kinetic energy of electrons ejected in each of the following cases
(i) if ultraviolet radiation of wavelength λ = 1.80 × 10-5 cm and
(ii) radiation of frequency 4 x 1015 Hz is made incident on the tungsten surface?
Radiation of wavelength 4500 Å is incident on a metal having work function 2.0 eV. Due to the presence of a magnetic field B, the most energetic photoelectrons emitted in a direction perpendicular to the field move along a circular path of radius 20 cm. What is the value of the magnetic field B?
The electrons are emitted in the photoelectric effect from a metal surface.
The maximum velocity of photoelectron emitted is 4.8 m/s. If the e/m ratio of the electron is 1.76 × 1011 C/kg, then stopping potential is given by ______
The kinetic energy of the most energetic photoelectron emitted from a metal surface is doubled when the wavelength of the incident radiation is reduced from λ1 to λ2. The work function of the metal is ______
The following graph shows the stopping potential V0 versus frequency v for photoelectric emission from two metals A and B. The slope of each of the lines gives ______
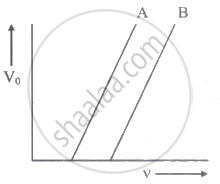
The maximum velocity of the photoelectron emitted by the metal surface is 'v '. Charge and mass of the photoelectron is denoted by 'e' and 'm' respectively. The stopping potential in volt is ______.
When a light of wavelength 4000 Å falls on a photoelectric emitter, photoelectrons are liberated. For another emitter, light of wavelength 6000 Å is sufficient for photo emission. The work functions of the two emitters are in the ratio of ____________.
A metal surface is illuminated by light of given intensity and frequency to cause photoemission. If the intensity of illumination is reduced to one-fourth of its original value then the maximum KE of the emitted photoelectrons would be ______.
In photoelectric effect, for a light of different intensities but of same frequency, the stopping potential for a given metal is ____________.
In photoelectric effect, graph of saturation current versus frequency of light is plotted. The nature of the graph will be ____________.
Light of frequency 2 times the threshold frequency is incident on a photo sensitive material. If the frequency is made `1/3`rd and intensity is doubled then the photocurrent will ______.
When light of wavelength 'λ' is incident on a photosensitive surface, the stopping potential is 'V'. When light of wavelength '3λ' is incident on the same surface, the stopping potential is `"V"/6`. Threshold wavelength for the surface is _______.
The photo electric effect to take place for a metal, the minimum frequency required is 5.792 × 1014 Hz. A light of wavelength 6000 Å is incident on that metal surface. What is the corresponding frequency of light and will there be photoelectric emissions? [velocity of light = 3 × 108 m/s]
Photoelectrons are emitted from a photosensitive surface for the light of wavelengths λ1 = 360 nm and λ2 = 600 nm. What is the ratio of work functions for lights of wavelength 'λ1' to 'λ2'?
The photon of frequency vis incident on a metal surface whose threshold frequency is v0. The kinetic energy of the emitted photoelectrons will be ______.
A metal surface having work function 'w0' emits photoelectrons when photons of energy 'E' are incident on it. The electron enters the uniform magnetic field (B) in perpendicular direction and moves in circular path of radius 'r'. Then 'r' is equal to (m and e be the mass and charge of electron respectively) ____________.
When the work function of a metal increases, maximum kinetic energy of emitted photoelectrons ____________.
Is it always necessary to use red light to get a photoelectric effect?
The radiation corresponding to the 3 → 2 transition of a hydrogen atom falls on a gold surface to generate photoelectrons. These electrons are passed through a magnetic field of 5 × 10-4 T. Assume that the radius of the largest circular path followed by these electrons is 7 mm, and the work function of the metal is ______.
(Mass of electron = 9.1 × 10-31 kg)
Photoelectrons are observed to just emit out of a material surface when the light of 620 nm falls on it with the intensity of 100 W m-2. If the light of wavelength 400 nm is incident on the same material with an intensity of 1 W m-2, what would be the minimum reverse potential needed to stop the outflow of the electrons?
The radiation emitted, when an electron jumps from n = 3 to n = 2 orbit is a hydrogen atom, falls on a metal to produce photoelectron. The electrons from the metal surface with maximum kinetic energy are made to move perpendicular to a magnetic field of `1/320`T in a radius of 10-3m. Find the 320 work function of metal:
Light of wavelength λ, which is less than threshold wavelength is incident on a photosensitive material. If incident wavelength is decreased so that emitted photoelectrons are moving with same velocity, then stopping potential will ______.
The photoelectric threshold for a certain metal surface is 3600 Å. If the metal surface is irradiated by a wavelength of 1100 Å, then kinetic energy of the emitted photoelectrons is ______.
Explain the formation of clouds at high altitude.
Explain the experimental set-up of photoelectric effect.
