Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
If the total charge enclosed by a surface is zero, does it imply that the elecric field everywhere on the surface is zero? Conversely, if the electric field everywhere on a surface is zero, does it imply that net charge inside is zero.
उत्तर
According to Gauss’ law, the flux associated with any closed surface is given by `int_s` E.dS = `q_(enclosed)/ε_0`. The term `q_(enclosed)` on the right side of the equation includes the sum of all charges enclosed by the surface called (Gaussian surface).
In the left side equation, the electric field is due to all the charges present both inside as well as outside the Gaussian surface.
Thus, despite being total charge enclosed by a surface zero, it doesn’t imply that the electric field everywhere on the surface is zero, the field may be normal to the surface.
Also, conversely if the electric field everywhere on a surface is zero.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
State and explain Gauss’s law.
A charge Q is placed at the centre of a cube. Find the flux of the electric field through the six surfaces of the cube.
Answer the following question.
State Gauss's law for magnetism. Explain its significance.
The surface considered for Gauss’s law is called ______.
Which of the following statements is not true about Gauss’s law?
Gauss' law helps in ______
The Electric flux through the surface
 (i) |
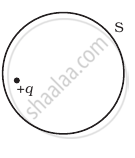 (ii) |
 (iii) |
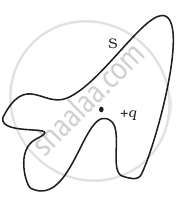 (iv) |
If `oint_s` E.dS = 0 over a surface, then ______.
- the electric field inside the surface and on it is zero.
- the electric field inside the surface is necessarily uniform.
- the number of flux lines entering the surface must be equal to the number of flux lines leaving it.
- all charges must necessarily be outside the surface.
