Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
In a parallel plate capacitor with air between the plates, each plate has an area of 6 × 10−3m2 and the separation between the plates is 3 mm.
- Calculate the capacitance of the capacitor.
- If this capacitor is connected to 100 V supply, what would be the charge on each plate?
- How would charge on the plates be affected, if a 3 mm thick mica sheet of k = 6 is inserted between the plates while the voltage supply remains connected?
उत्तर
Here, A = 6 × 10–3m2, d = 3 mm = 3 × 10–3m
- Capacitance, C = `(∈_0A)/d`
= `((8.85 xx 10^-12 xx 6 xx 10^-3))/(3 xx 10^-3)`
= 17.7 × 10–12F - Charge, Q = CV
= 17.7 × 10–12 × 100
= 17.7 × 10–10C - New charge Q' = KQ
= 6 × 17.7 × 10–10
= 1.062 × 10–8C
संबंधित प्रश्न
In a parallel plate capacitor with air between the plates, each plate has an area of 6 × 10−3 m2 and the distance between the plates is 3 mm. Calculate the capacitance of the capacitor. If this capacitor is connected to a 100 V supply, what is the charge on each plate of the capacitor?
The plates of a parallel plate capacitor have an area of 90 cm2 each and are separated by 2.5 mm. The capacitor is charged by connecting it to a 400 V supply.
(a) How much electrostatic energy is stored by the capacitor?
(b) View this energy as stored in the electrostatic field between the plates, and obtain the energy per unit volume u. Hence arrive at a relation between u and the magnitude of electric field E between the plates.
Show that the force on each plate of a parallel plate capacitor has a magnitude equal to `(1/2)` QE, where Q is the charge on the capacitor, and E is the magnitude of the electric field between the plates. Explain the origin of the factor `1/2`.
A parallel plate capacitor is to be designed with a voltage rating 1 kV, using a material of dielectric constant 3 and dielectric strength about 107 Vm−1. (Dielectric strength is the maximum electric field a material can tolerate without breakdown, i.e., without starting to conduct electricity through partial ionisation.) For safety, we should like the field never to exceed, say 10% of the dielectric strength. What minimum area of the plates is required to have a capacitance of 50 pF?
Define the capacitance of a capacitor. Obtain the expression for the capacitance of a parallel plate capacitor in vacuum in terms of plate area A and separation d between the plates.
A slab of material of dielectric constant K has the same area as that of the plates of a parallel plate capacitor but has the thickness d/2, where d is the separation between the plates. Find out the expression for its capacitance when the slab is inserted between the plates of the capacitor.
Define the capacitance of a capacitor and its SI unit.
A parallel-plate capacitor has plate area 20 cm2, plate separation 1.0 mm and a dielectric slab of dielectric constant 5.0 filling up the space between the plates. This capacitor is joined to a battery of emf 6.0 V through a 100 kΩ resistor. Find the energy of the capacitor 8.9 μs after the connections are made.
For a one dimensional electric field, the correct relation of E and potential V is _________.
A parallel plate capacitor is connected to a battery as shown in figure. Consider two situations:
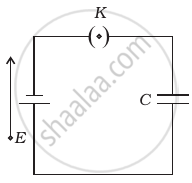
- Key K is kept closed and plates of capacitors are moved apart using insulating handle.
- Key K is opened and plates of capacitors are moved apart using insulating handle.
Choose the correct option(s).
- In A: Q remains same but C changes.
- In B: V remains same but C changes.
- In A: V remains same and hence Q changes.
- In B: Q remains same and hence V changes.
