Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
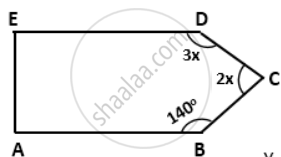
In a pentagon ABCDE, AB || ED and ∠B = 140°, ∠C = 2x° and ∠D = 3x°. Find ∠C and ∠D
उत्तर
Since AB || ED, we have
∠A + ∠E = 180°
Now,
∠A + ∠B + ∠C + ∠D + ∠E = (5 - 2) x 180°
⇒ (∠A + ∠E) + 140° + 2x + 3x = 3 x 180°
⇒ 180° + 140° + 5x = 540°
⇒ 320° + 5x = 540°
⇒ 5x = 220°
⇒ x = 44°
Hence,
∠C = 2x = 2 x 44° = 88°
∠D = 3x = 3 x 44° = 132°.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
What is the sum of the measures of the angels of a convex quadrilateral? Will this property hold if the quadrilateral is not convex? (Make a non-convex quadrilateral and try!)
In a quadrilateral, define of the following Angles .
Mark the correct alternative in each of the following:
The opposite sides of a quadrilateral have
Angle A of an isosceles trapezium ABCD is 115°; find the angles B, C and D.
In a parallelogram ABCD, its diagonals AC and BD intersect each other at point O.
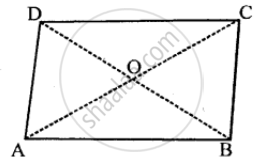
If AC = 12 cm and BD = 9 cm ; find; lengths of OA and OD.
In the quadrilateral ABCD, AB = BC and AD = DC Measure of ∠BCD is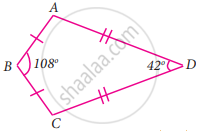
If angles A, B, C and D of the quadrilateral ABCD, taken in order, are in the ratio 3 : 7 : 6 : 4, then ABCD is a ______.
If APB and CQD are two parallel lines, then the bisectors of the angles APQ, BPQ, CQP and PQD form ______.
Using the information given, name the right angles in part of figure:
AC ⊥ BD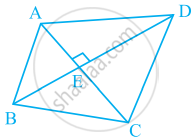
Draw a rough sketch of a quadrilateral PQRS. Draw its diagonals. Name them. Is the meeting point of the diagonals in the interior or exterior of the quadrilateral?