Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
In a series LCR circuit, the phase difference between the voltage and the current is 45°. Then the power factor will be ______.
पर्याय
0.607
0.707
0.808
1
उत्तर
In a series LCR circuit, the phase difference between the voltage and the current is 45°. Then the power factor will be 0.707.
Explanation:
Let, Inductance = L
Conductance = C
Resistance = R
Frequency = f
Phase Difference between current and voltage = `phi`
As, in LCR circuit,
Power Factor = `cos phi`
Substitute the given values from,
`phi = 45^circ`
`cos 45^circ = 1/sqrt(2)`
Therefore, P.F = 0.707
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Obtain an expression for average power dissipated in a purely resistive A.C. circult.
A resistor of 500 Ω and an inductance of 0.5 H are in series with an AC source which is given by V = `100 sqrt2` sin (1000 t). The power factor of the combination is ______.
An AC source generating a voltage e = e0sinωt is connected to a capacitor of capacitance C. Find the expression for the current i flowing through it. Plot a graph of e and i versus ωt.
A light bulb is rated 100W for 220 V AC supply of 50 Hz. Calculate
- resistance of the bulb.
- the rms current through the bulb
An AC circuit consists of only an inductor of inductance 2 H. If the current is represented by a sine wave of amplitude 0.25 A and frequency 60 Hz, calculate the effective potential difference across the inductor. (π = 3.142)
Alternating emf of e = 220 sin 100 πt is applied to a circuit containing an inductance of (1/π) henry. Write an equation for instantaneous current through the circuit. What will be the reading of the AC galvanometer connected in the circuit?
A 25 μF capacitor, a 0.10 H inductor, and a 25Ω resistor are connected in series with an AC source whose emf is given by e = 310 sin 314 t (volt). What is the frequency, reactance, impedance, current, and phase angle of the circuit?
A 100 μF capacitor is charged with a 50 V source supply. Then source supply is removed and the capacitor is connected across an inductance, as a result of which 5A current flows through the inductance. Calculate the value of the inductance.
What is meant by wattles current?
Give any one definition of power factor.
An alternating e.m.f. of 0.2 V is applied across an LCR series circuit having R = 4 `Omega`, C = 80 µF and L = 200 mH. At resonance the voltage drop across the inductor is ____________.
In series 'LR' circuit and in series 'RC' circuit, same current is flowing. If the frequency of e.m.f. of a.c. is increased for both the circuits, the impedance will ____________.
In series LCR circuit, resistance is 18 `Omega` and impedance is 33 `Omega`. An r.m.s. voltage of 220 V is applied across the circuit. The true power consumed in a.c. circuit is ____________.
In LCR series circuit, an alternating e.m.f. 'e' and current 'i' are given by the equations e = 100 sin (100 t) volt,
`"i" = 100 "sin" (100"t" + pi/3)"mA"`.
The average power dissipated in the circuit will be ____________.
An e.m.f. E = E0 sin `omega`t is applied to a circuit containing 'L' and 'R' in series. If XL = R, then the power dissipated in the circuit is ____________.
The voltage gain of a CE amplifier is 50. A sinusoidal ac of amplitude 10 mV is applied as a signal. The output of the amplifier will be ______.
In a series LR circuit XL = R and power factor of the circuit is P1. When capacitor with capacitance C such that XL= XC is put in series, the power factor becomes P2. The ratio `"P"_1/"P"_2` is ______.
In series LCR circuit R = 18 Ω and impedance is 33 Ω An rms voltage 220V is applied across the circuit. The ture power consumed in AC circuit is ______.
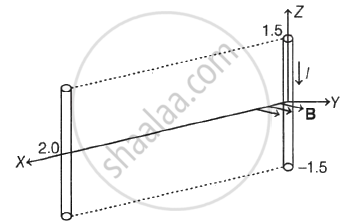
A conductor lies along the Z-axis at −1.5 ≤ Z ≤ 1.5 m and carries a fixed current of 10.0 A in −az direction as (see figure). For a field B = 3.0 × 10−4`"e"^(−0.2"x")`ay T, find the power required to move the conductor at constant speed to x = 2.0 m, y = 0 in 5 × 10−3 s. Assume parallel motion along the x-axis.
What is the average value of alternating current over a complete cycle?
The power factor of LCR circuit is ______.
Explain the theory of an AC circuit with a resistor.
Where is the power dissipated in an alternating current circuit?
