Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
In any ac circuit, is the applied instantaneous voltage equal to the algebraic sum of the instantaneous voltages across the series elements of the circuit? Is the same true for rms voltage?
उत्तर
Yes; the statement is not true for rms voltage.
It is true that in any ac circuit, the applied voltage is equal to the average sum of the instantaneous voltages across the series elements of the circuit. However, this is not true for rms voltage because voltages across different elements may not be in phase.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Define electric resonance.
Derive an expression for phase angle between the applied voltage and current in a series RLC circuit.
When does power factor of a series RLC circuit become maximum?
Why is choke coil needed in the use of fluorescent tubes with ac mains? Why can we not use an ordinary resistor instead of the choke coil?
The rms current Irms is related to the peak current Io as ______.
The capacitive reactance in an A.C. circuit is ______.
An inductor coil stores 64 J of magnetic field energy and dissipates energy at the rate of 640 W when a current of 8 A is passed through it. If this coil is joined across an ideal battery, find the time constant of the circuit in seconds ______.
A capacitor and resistor are connected with an AC source as shown in figure. Reactance of capacitor is XC = 3 Ω and resistance of resistor is 4 Ω. Phase difference between current I and I1 is approx ______.
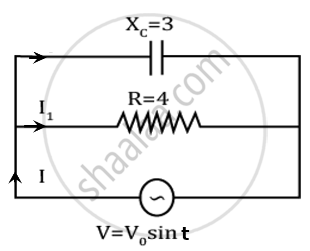
A 50 Hz AC source of 20 volts is connected across R and C as shown in figure. The voltage across R is 12 volt. The voltage across c is ______.
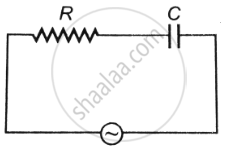
An alternating current I = 14 sin (100 πt) A passes through a series combination of a resistor of 30 Ω and an inductor of `(2/(5pi))` H. Taking `sqrt2` = 1.4 calculate the rms value of the voltage drops across the resistor and the inductor.
